Reduced IgG anti-small nuclear ribonucleoprotein autoantibody production in systemic lupus erythematosus patients with positive IgM anti-cytomegalovirus antibodies
- PMID: 19232124
- PMCID: PMC2688261
- DOI: 10.1186/ar2621
Reduced IgG anti-small nuclear ribonucleoprotein autoantibody production in systemic lupus erythematosus patients with positive IgM anti-cytomegalovirus antibodies
Abstract
Introduction: Systemic lupus erythematosus is characterized by production of autoantibodies to RNA or DNA-protein complexes such as small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNPs). A role of Epstein-Barr virus in the pathogenesis has been suggested. Similar to Epstein-Barr virus, cytomegalovirus (CMV) infects the majority of individuals at a young age and establishes latency with a potential for reactivation. Homology of CMV glycoprotein B (UL55) with the U1snRNP-70 kDa protein (U1-70 k) has been described; however, the role of CMV infection in production of anti-snRNPs is controversial. We investigated the association of CMV serology and autoantibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus.
Methods: Sixty-one Mexican patients with systemic lupus erythematosus were tested for CMV and Epstein-Barr virus serology (viral capsid antigen, IgG, IgM) and autoantibodies by immunoprecipitation and ELISA (IgG and IgM class, U1RNP/Sm, U1-70 k, P peptide, rheumatoid factor, dsDNA, beta2-glycoprotein I).
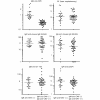
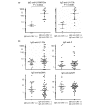
Results: IgG anti-CMV and IgM anti-CMV were positive in 95% (58/61) and 33% (20/61), respectively, and two cases were negative for both. Clinical manifestation and autoantibodies in the IgM anti-CMV+ group (n = 20) versus the IgM anti-CMV(-)IgG+ (n = 39) group were compared. Most (19/20) of the IgM anti-CMV+ cases were IgG anti-CMV+, consistent with reactivation or reinfection. IgM anti-CMV was unrelated to rheumatoid factor or IgM class autoantibodies and none was positive for IgM anti-Epstein-Barr virus-viral capsid antigen, indicating that this is not simply due to false positive results caused by rheumatoid factor or nonspecific binding by certain IgM. The IgM anti-CMV+ group has significantly lower levels of IgG anti-U1RNP/Sm and IgG anti-U1-70 k (P = 0.0004 and P = 0.0046, respectively). This finding was also confirmed by immunoprecipitation. Among the IgM anti-CMV(-) subset, anti-Su was associated with anti-U1RNP and anti-Ro (P < 0.05). High levels of IgG anti-CMV were associated with production of lupus-related autoantibodies to RNA or DNA-protein complex (P = 0.0077).
Conclusions: Our findings suggest a potential role of CMV in regulation of autoantibodies to snRNPs and may provide a unique insight to understand the pathogenesis.
Figures
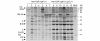
References
-
- Reeves WH, Narain S, Satoh M. Autoantibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. In: Koopman WJ, Moreland LW, editor. Arthritis and Allied Conditions A Textbook of Rheumatology. 15. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; 2005. pp. 1497–1521.
-
- Denman AM. Systemic lupus erythematosus – is a viral aetiology a credible hypothesis? J Infect. 2000;40:229–233. - PubMed
-
- Barzilai O, Ram M, Shoenfeld Y. Viral infection can induce the production of autoantibodies. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2007;19:636–643. - PubMed
-
- Poole BD, Scofield RH, Harley JB, James JA. Epstein–Barr virus and molecular mimicry in systemic lupus erythematosus. Autoimmunity. 2006;39:63–70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

