Niemann-Pick C2 (NPC2) and intracellular cholesterol trafficking
- PMID: 19232397
- PMCID: PMC4281484
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2009.02.001
Niemann-Pick C2 (NPC2) and intracellular cholesterol trafficking
Abstract
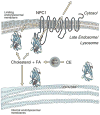
Cholesterol is an important precursor for numerous biologically active molecules, and it plays a major role in membrane structure and function. Cholesterol can be endogenously synthesized or exogenously taken up via the endocytic vesicle system and subsequently delivered to post-endo/lysosomal sites including the plasma membrane and the endoplasmic reticulum. Niemann-Pick C (NPC) disease results in the accumulation of exogenously-derived cholesterol, as well as other lipids, in late endosomes and lysosomes (LE/LY). Identification of the two genes that underlie NPC disease, NPC1 and NPC2, has focused attention on the mechanisms by which lipids, in particular cholesterol, are transported out of the LE/LY compartment. This review discusses the role of the NPC2 protein in cholesterol transport, and the potential for concerted action of NPC1 and NPC2 in regulating normal intracellular cholesterol homeostasis.
Figures

References
-
- Chang TY, Chang CC, Ohgami N, Yamauchi Y. Cholesterol sensing, trafficking, and esterification. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2006;22:129–157. - PubMed
-
- Wustner D, Mondal M, Tabas I, Maxfield FR. Direct observation of rapid internalization and intracellular transport of sterol by macrophage foam cells. Traffic. 2005;6:396–412. - PubMed
-
- Lange Y, Ye J, Steck TL. Activation of membrane cholesterol by displacement from phospholipids. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:36126–36131. - PubMed
-
- Maxfield FR, Menon AK. Intracellular sterol transport and distribution. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2006;18:379–385. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

