Lipoic acid improves hypertriglyceridemia by stimulating triacylglycerol clearance and downregulating liver triacylglycerol secretion
- PMID: 19232511
- PMCID: PMC2771166
- DOI: 10.1016/j.abb.2009.01.024
Lipoic acid improves hypertriglyceridemia by stimulating triacylglycerol clearance and downregulating liver triacylglycerol secretion
Abstract
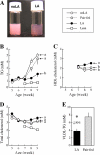
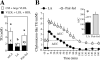
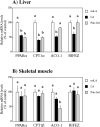
Elevated blood triacylglycerol (TG) is a significant contributing factor to the current epidemic of obesity-related health disorders, including type-2 diabetes, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, and cardiovascular disease. The observation that mice lacking the enzyme sn-glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase are protected from insulin resistance suggests the possibility that the regulation of TG synthesis be a target for therapy. Five-week-old Zucker Diabetic Fatty (ZDF) rats were fed a diet containing (R)-alpha-lipoic acid (LA, approximately 200mg/kg body weight per day) for 5 weeks. LA offset the rise in blood and liver TG by inhibiting liver lipogenic gene expression (e.g. sn-glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase-1 and diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase-2), lowering hepatic TG secretion, and stimulating clearance of TG-rich lipoproteins. LA-induced TG lowering was not due to the anorectic properties of LA, as pair-fed rats developed hypertriglyceridemia. Livers from LA-treated rats exhibited elevated glycogen content, suggesting dietary carbohydrates were stored as glycogen rather than becoming lipogenic substrate. Although AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) reportedly mediates the metabolic effects of LA in rodents, no change in AMPK activity was observed, suggesting LA acted independently of this kinase. The hepatic expression of peroxisome proliferator activated receptor alpha (PPARalpha) target genes involved in fatty acid beta-oxidation was either unchanged or decreased with LA, indicating a different mode of action than for fibrate drugs. Given its strong safety record, LA may have potential clinical applications for the treatment or prevention of hypertriglyceridemia and diabetic dyslipidemia.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Reversal of obesity-induced hypertriglyceridemia by (R)-α-lipoic acid in ZDF (fa/fa) rats.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013 Sep 27;439(3):390-5. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.08.063. Epub 2013 Aug 29. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013. PMID: 23994635
-
Alpha-lipoic acid reduces LDL-particle number and PCSK9 concentrations in high-fat fed obese Zucker rats.PLoS One. 2014 Mar 4;9(3):e90863. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0090863. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24595397 Free PMC article.
-
Improvement of mTORC1-driven overproduction of apoB-containing triacylglyceride-rich lipoproteins by short-chain fatty acids, 4-phenylbutyric acid and (R)-α-lipoic acid, in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Mar;1861(3):166-76. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2015.12.001. Epub 2015 Dec 8. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26680362
-
α-Lipoic acid as a triglyceride-lowering nutraceutical.Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2015 Dec;93(12):1029-41. doi: 10.1139/cjpp-2014-0480. Epub 2015 Apr 20. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26235242 Review.
-
Omega-3 fatty acids eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid and their mechanisms of action on apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins in humans: a review.Lipids Health Dis. 2017 Aug 10;16(1):149. doi: 10.1186/s12944-017-0541-3. Lipids Health Dis. 2017. PMID: 28797250 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
α-Lipoic Acid Ameliorates Arsenic-Induced Lipid Disorders by Promoting Peroxisomal β-Oxidation and Reducing Lipophagy in Chicken Hepatocyte.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025 Mar;12(11):e2413255. doi: 10.1002/advs.202413255. Epub 2025 Jan 30. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025. PMID: 39887668 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of different doses of atorvastatin treatment on serum levels of 8-hydroxy-guanin (8-OHdG) and cardiac function in patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy.Pak J Med Sci. 2015 Jan-Feb;31(1):37-42. doi: 10.12669/pjms.311.5840. Pak J Med Sci. 2015. PMID: 25878611 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of lipoic acid on apelin in 3T3-L1 adipocytes and in high-fat fed rats.J Physiol Biochem. 2011 Sep;67(3):479-86. doi: 10.1007/s13105-011-0087-1. Epub 2011 Apr 2. J Physiol Biochem. 2011. PMID: 21461750
-
Chronic treatment of (R)-α-lipoic acid reduces blood glucose and lipid levels in high-fat diet and low-dose streptozotocin-induced metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes in Sprague-Dawley rats.Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2017 Apr 3;5(3):e00306. doi: 10.1002/prp2.306. eCollection 2017 Jun. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2017. PMID: 28603627 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Dietary L-carnosine and Alpha-lipoic Acid on Growth Performance, Blood Thyroid Hormones and Lipid Profiles in Finishing Pigs.Asian-Australas J Anim Sci. 2015 Oct;28(10):1465-70. doi: 10.5713/ajas.14.0604. Asian-Australas J Anim Sci. 2015. PMID: 26194221 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ford ES, Giles WH, Dietz WH. Prevalence of the metabolic syndrome among US adults: findings from the third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Jama. 2002;287:356–359. - PubMed
-
- Taskinen MR. Diabetic dyslipidaemia: from basic research to clinical practice. Diabetologia. 2003;46:733–749. - PubMed
-
- Athyros VG, Giouleme OI, Nikolaidis NL, Vasiliadis TV, Bouloukos VI, Kontopoulos AG, Eugenidis NP. Long-term follow-up of patients with acute hypertriglyceridemia-induced pancreatitis. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2002;34:472–475. - PubMed
-
- Parekh S, Anania FA. Abnormal lipid and glucose metabolism in obesity: implications for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology. 2007;132:2191–2207. - PubMed
-
- Austin MA, Hokanson JE, Edwards KL. Hypertriglyceridemia as a cardiovascular risk factor. Am J Cardiol. 1998;81:7B–12B. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

