SYNCRIP (synaptotagmin-binding, cytoplasmic RNA-interacting protein) is a host factor involved in hepatitis C virus RNA replication
- PMID: 19232660
- PMCID: PMC3099193
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2009.01.018
SYNCRIP (synaptotagmin-binding, cytoplasmic RNA-interacting protein) is a host factor involved in hepatitis C virus RNA replication
Abstract
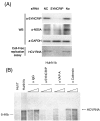
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) RNA replication requires viral nonstructural proteins as well as cellular factors. Recently, a cellular protein, synaptotagmin-binding, cytoplasmic RNA-interacting protein (SYNCRIP), also known as NSAP1, was found to bind HCV RNA and enhance HCV IRES-dependent translation. We investigate whether this protein is also involved in the HCV RNA replication. We found that SYNCRIP was associated with detergent-resistant membrane fractions and colocalized with newly-synthesized HCV RNA. Knock-down of SYNCRIP by siRNA significantly decreased the amount of HCV RNA in the cells containing a subgenomic replicon or a full-length viral RNA. Lastly, an in vitro replication assay after immunodepletion of SYNCRIP showed that SYNCRIP was directly involved in HCV RNA replication. These findings indicate that SYNCRIP has dual functions, participating in both RNA replication and translation in HCV life cycle.
Figures




References
-
- Aizaki H., Lee K.J., Sung V.M., Ishiko H., Lai M.M. Characterization of the hepatitis C virus RNA replication complex associated with lipid rafts. Virology. 2004;324(2):450–461. - PubMed
-
- Aizaki H., Choi K.S., Liu M., Li Y.J., Lai M.M. Polypyrimidine-tract-binding protein is a component of the HCV RNA replication complex and necessary for RNA synthesis. J. Biomed. Sci. 2006;13(4):469–480. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

