FMR1: a gene with three faces
- PMID: 19233246
- PMCID: PMC2692361
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2009.02.007
FMR1: a gene with three faces
Abstract
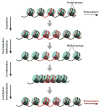
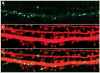
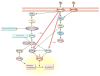
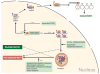
The FMR1 gene is involved in three different syndromes, the fragile X syndrome (FXS), premature ovarian insufficiency (POI) and the fragile X-associated tremor/ataxia syndrome (FXTAS) at older age. Fragile X syndrome is caused by an expansion of a CGG repeat above 200 units in the FMR1 gene resulting in the absence of the FMR1 mRNA and protein. The FMR1 protein is proposed to act as a regulator of mRNA transport and of translation of target mRNAs at the synapse. FXS is seen as a loss of function disorder. POI and FXTAS are found in individuals with an expanded repeat between 50 and 200 CGGs and are associated with increased FMR1 mRNA levels. The presence of elevated FMR1 mRNA in FXTAS suggests that FXTAS may represent a toxic RNA gain-of-function effect. The molecular basis of POI is yet unknown. The role of the FMR1 gene in these disorders is discussed.
Figures

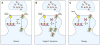
References
-
- Hagerman RJ. The physical and behavioural phenotype. In: Hagerman RJ, Hagerman P, editors. Fragile-X syndrome: diagnosis, treatment and research. The Johns Hopkins University Press; Baltimore: 2002. pp. 3–109.
-
- Sherman SL, Jacobs PA, Morton NE, Froster-Iskenius U, Howard-Peebles PN, Nielsen KB, Partington MW, Sutherland GR, Turner G, Watson M. Further segregation analysis of the fragile X syndrome with special reference to transmitting males. Hum Genet. 1985;69:289–299. - PubMed
-
- Verkerk AJ, Pieretti M, Sutcliffe JS, Fu YH, Kuhl DP, Pizzuti A, Reiner O, Richards S, Victoria MF, Zhang FP, Eussen BE, Van Ommen GJB, Blonden LAJ, Riggins GJ, Chastain JL, Kunst CB, Galjaard H, Caskey CT, Nelson DL, Oostra BA, Warren ST. Identification of a gene (FMR-1) containing a CGG repeat coincident with a breakpoint cluster region exhibiting length variation in fragile X syndrome. Cell. 1991;65:905–914. - PubMed
-
- Fu YH, Kuhl DP, Pizzuti A, Pieretti M, Sutcliffe JS, Richards S, Verkerk AJ, Holden JJ, Fenwick R, Jr, Warren ST, Oostra BA, Nelson DL, Caskey CT. Variation of the CGG repeat at the fragile X site results in genetic instability: resolution of the Sherman paradox. Cell. 1991;67:1047–1058. - PubMed
-
- Oberlé I, Rousseau F, Heitz D, Kretz C, Devys D, Hanauer A, Boue J, Bertheas MF, Mandel JL. Instability of a 550-base pair DNA segment and abnormal methylation in fragile X syndrome. Science. 1991;252:1097–1102. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

