Upregulation of IL-6, IL-8 and CCL2 gene expression after acute inflammation: Correlation to clinical pain
- PMID: 19233564
- PMCID: PMC3513699
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pain.2009.02.001
Upregulation of IL-6, IL-8 and CCL2 gene expression after acute inflammation: Correlation to clinical pain
Abstract
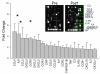
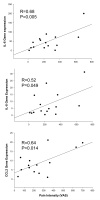
Tissue injury initiates a cascade of inflammatory mediators and hyperalgesic substances including prostaglandins, cytokines and chemokines. Using microarray and qRT-PCR gene expression analyses, the present study evaluated changes in gene expression of a cascade of cytokines following acute inflammation and the correlation between the changes in the gene expression level and pain intensity in the oral surgery model of tissue injury and acute pain. Tissue injury resulted in a significant upregulation in the gene expression of interleukin-6 (IL-6; 63.3-fold), IL-8 (8.1-fold), chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2 (CCL2; 8.9-fold), chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 1 (CXCL1; 30.5-fold), chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 2 (CXCL2; 26-fold) and annexin A1 (ANXA1; 12-fold). The upregulation of IL-6 gene expression was significantly correlated to the upregulation of IL-8, CCL2, CXCL1 and CXCL2 gene expression. Interestingly, the tissue injury-induced upregulation of IL-6, IL-8 and CCL2 gene expression, was positively correlated to pain intensity at 3h post-surgery, the onset of acute inflammatory pain. However, ketorolac treatment did not have a significant effect on the gene expression of IL-6, IL-8, CCL2, CXCL2 and ANXA1 at the same time point of acute inflammation. These results demonstrate that the upregulation of IL-6, IL-8 and CCL2 gene expression contributes to the development of acute inflammation and inflammatory pain. The lack of effect of ketorolac on the expression of these gene products may be related to the ceiling analgesic effects of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Figures


References
-
- Brown Z, Strieter RM, Chensue SW, Ceska M, Lindley I, Neild GH, Kunkel SL, Westwick J. Cytokine-activated human mesangial cells generate the neutrophil chemoattractant, interleukin 8. Kidney Int. 1991;40:86–90. - PubMed
-
- Buvanendran A, Kroin JS, Berger RA, Hallab NJ, Saha C, Negrescu C, Moric M, Caicedo MS, Tuman KJ. Upregulation of prostaglandin E2 and interleukins in the central nervous system and peripheral tissue during and after surgery in humans. Anesthesiology. 2006;104:403–410. - PubMed
-
- Carvalho B, Clark DJ, Angst MS. Local and systemic release of cytokines, nerve growth factor, prostaglandin E2, and substance P in incisional wounds and serum following cesarean delivery. J Pain. 2008 [Epub ahead of print] doi:10.1016/j.jpain.2008.02.004. - PubMed
-
- Chen C-C, Mo F-E, Lau LF. The angiogenic factor Cyr61 activates a genetic program for wound healing in human skin fibroblasts. J. Biol. Chem. 2001;276:47329–47337. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

