IL-17F: regulation, signaling and function in inflammation
- PMID: 19233684
- PMCID: PMC2663007
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cyto.2008.12.024
IL-17F: regulation, signaling and function in inflammation
Abstract
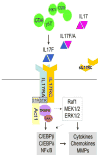
The IL-17 cytokine family is composed of six members. IL-17F, discovered in 2001, recently has drawn increasing attention due to its greatest similarity to IL-17, a widely recognized inflammatory cytokine. The genes encoding IL-17 and IL-17F are localized in the same chromosomal region and are co-expressed by CD4+ and gammadelta T cells. IL-17F can be secreted as homodimers or heterodimers with IL-17. Similar to IL-17, IL-17F utilizes IL-17RA and IL-17RC as its receptor and employs Act1 and TRAF6 as its signal transducers to induce the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines in many different cell types. However, mice lacking either IL-17 or IL-17F exhibit distinct defects in experimental models of asthma and colitis. These results have laid the basis to understand the role of IL-17F in the pathogenesis of human diseases.
Figures
References
-
- Moseley TA, Haudenschild DR, Rose L, Reddi AH. Interleukin-17 family and IL-17 receptors. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2003;14:155–74. - PubMed
-
- Fort MM, Cheung J, Yen D, Li J, Zurawski SM, Lo S, Menon S, Clifford T, Hunte B, Lesley R, Muchamuel T, Hurst SD, Zurawski G, Leach MW, Gorman DM, Rennick DM. IL-25 induces IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 and Th2-associated pathologies in vivo. Immunity. 2001;15:985–95. - PubMed
-
- Kawaguchi M, Onuchic LF, Li XD, Essayan DM, Schroeder J, Xiao HQ, Liu MC, Krishnaswamy G, Germino G, Huang SK. Identification of a novel cytokine, ML-1, and its expression in subjects with asthma. J Immunol. 2001;167:4430–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

