Characterization of the polyoxin biosynthetic gene cluster from Streptomyces cacaoi and engineered production of polyoxin H
- PMID: 19233844
- PMCID: PMC2667750
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M807534200
Characterization of the polyoxin biosynthetic gene cluster from Streptomyces cacaoi and engineered production of polyoxin H
Abstract
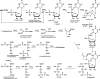
A gene cluster (pol) essential for the biosynthesis of polyoxin, a nucleoside antibiotic widely used for the control of phytopathogenic fungi, was cloned from Streptomyces cacaoi. A 46,066-bp region was sequenced, and 20 of 39 of the putative open reading frames were defined as necessary for polyoxin biosynthesis as evidenced by its production in a heterologous host, Streptomyces lividans TK24. The role of PolO and PolA in polyoxin synthesis was demonstrated by in vivo experiments, and their functions were unambiguously characterized as O-carbamoyltransferase and UMP-enolpyruvyltransferase, respectively, by in vitro experiments, which enabled the production of a modified compound differing slightly from that proposed earlier. These studies should provide a solid foundation for the elucidation of the molecular mechanisms for polyoxin biosynthesis, and set the stage for combinatorial biosynthesis using genes encoding different pathways for nucleoside antibiotics.
Figures
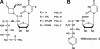






References
-
- Isono, K. (1988) J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 41 1711-1739 - PubMed
-
- Isono, K., Nagatsu, J., Kobinata, K., Sazuki, K., and Suzuki, S. (1965) Agric. Biol. Chem. 29 848-854
-
- Isono, K. N., Kobinata, K., Sasaki, K., and Suzuki, S. (1967) Agric. Biol. Chem. 31 190-199
-
- Wen, Z. (2004) Chinese J. Biol. 21 36-37
-
- Hori, M., Eguchi, J., Kakiki, K., and Misato, T. (1974) J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 27 260-266 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

