Anti-inflammatory role of IL-17 in experimental autoimmune uveitis
- PMID: 19234216
- PMCID: PMC3275433
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.0802487
Anti-inflammatory role of IL-17 in experimental autoimmune uveitis
Abstract
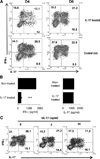
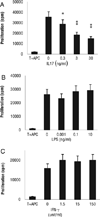
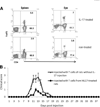
Previous studies have shown that IL-17 is a strong proinflammatory cytokine and that IL-17-producing autoreactive T cells play a major role in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases. In a previous study, we showed that injection of experimental autoimmune uveitis-susceptible mice with anti-IL-17 Abs blocked subsequent disease development. To determine whether administration of IL-17 to experimental autoimmune uveitis-susceptible Lewis rats and B10RIII mice injected with disease-inducing peptides enhanced disease susceptibility, we injected the recipient animals with various doses of human rIL-17 (hIL-17). Unexpectedly, the treated animals showed significant amelioration of disease; in addition, both the intensity of the autoreactive response and cytokine production by the autoreactive T cells induced by immunization with uveitogenic peptides were significantly decreased. Our results show that IL-17 has anti-inflammatory activity and that this cytokine can suppress the development of autoimmune disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Mangan PR, Harrington LE, O’Quinn DB, Helms WS, Bullard DC, Elson CO, Hatton RD, Wahl SM, Schoeb TR, Weaver CT. Transforming growth factor-β induces development of the TH17 lineage. Nature. 2006;441:231–234. - PubMed
-
- Bailey SL, Schreiner B, McMahon EJ, Miller SD. CNS myeloid DCs presenting endogenous myelin peptides “preferentially” polarize CD4+ TH-17 cells in relapsing EAE. Nat. Immunol. 2007;8:172–180. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

