Identification of a chemical probe for NAADP by virtual screening
- PMID: 19234453
- PMCID: PMC2659327
- DOI: 10.1038/nchembio.150
Identification of a chemical probe for NAADP by virtual screening
Abstract
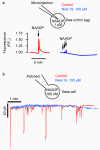
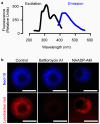
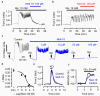
Research into the biological role of the Ca(2+)-releasing second messenger NAADP (nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide phosphate) has been hampered by a lack of chemical probes. To find new chemical probes for exploring NAADP signaling, we turned to virtual screening, which can evaluate millions of molecules rapidly and inexpensively. We used NAADP as the query ligand to screen the chemical library ZINC for compounds with similar three-dimensional shape and electrostatic properties. We tested the top-ranking hits in a sea urchin egg bioassay and found that one hit, Ned-19, blocks NAADP signaling at nanomolar concentrations. In intact cells, Ned-19 blocked NAADP signaling and fluorescently labeled NAADP receptors. Moreover, we show the utility of Ned-19 as a chemical probe by using it to demonstrate that NAADP is a key causal link between glucose sensing and Ca(2+) increases in mouse pancreatic beta cells.
Figures



References
-
- Lee HC. Nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NAADP)-mediated calcium signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2005;280:33693–6. - PubMed
-
- Lee HC, Aarhus R. A derivative of NADP mobilizes calcium stores insensitive to inositol trisphosphate and cyclic ADP-ribose. J. Biol. Chem. 1995;270:2152–7. - PubMed
-
- Giniatullin R, Nistri A, Yakel JL. Desensitization of nicotinic ACh receptors: shaping cholinergic signaling. Trend. Pharm. Sci. 2005;283:371–378. - PubMed
-
- Cancela JM, Churchill GC, Galione A. Coordination of agonist-induced Ca2+-signalling patterns by NAADP in pancreatic acinar cells. Nature. 1999;398:74–76. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- PubChem-Substance/56475047
- PubChem-Substance/56475048
- PubChem-Substance/56475049
- PubChem-Substance/56475050
- PubChem-Substance/56475051
- PubChem-Substance/56475052
- PubChem-Substance/56475053
- PubChem-Substance/56475054
- PubChem-Substance/56475055
- PubChem-Substance/56475056
- PubChem-Substance/56475057
- PubChem-Substance/56475058
- PubChem-Substance/56475059
- PubChem-Substance/56475060
- PubChem-Substance/56475061
- PubChem-Substance/56475062
- PubChem-Substance/56475063
- PubChem-Substance/56475064
- PubChem-Substance/56475065
- PubChem-Substance/56475066
- PubChem-Substance/56475067
- PubChem-Substance/56475068
- PubChem-Substance/56475069
- PubChem-Substance/56475070
- PubChem-Substance/56475071
- PubChem-Substance/56475072
- PubChem-Substance/56475073
- PubChem-Substance/56475074
- PubChem-Substance/56475075
- PubChem-Substance/56475076
- PubChem-Substance/56475077
- PubChem-Substance/56475078
- PubChem-Substance/56475079
- PubChem-Substance/56475080
- PubChem-Substance/56475081
- PubChem-Substance/56475082
- PubChem-Substance/56475083
- PubChem-Substance/56475084
- PubChem-Substance/56475085
- PubChem-Substance/56475086
- PubChem-Substance/56475087
- PubChem-Substance/56475088
- PubChem-Substance/56475089
- PubChem-Substance/56475090
- PubChem-Substance/56475091
- PubChem-Substance/56475092
- PubChem-Substance/56475093
- PubChem-Substance/56475094
- PubChem-Substance/56475095
- PubChem-Substance/56475096
- PubChem-Substance/56475097
- PubChem-Substance/56475098
- PubChem-Substance/56475099
- PubChem-Substance/56475100
- PubChem-Substance/56475101
- PubChem-Substance/56475102
- PubChem-Substance/56475103
- PubChem-Substance/56475104
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

