Structural insights into the substrate binding and stereoselectivity of giardia fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase
- PMID: 19236002
- PMCID: PMC2666783
- DOI: 10.1021/bi9001166
Structural insights into the substrate binding and stereoselectivity of giardia fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase
Abstract
Giardia lamblia fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase (FBPA) is a member of the class II zinc-dependent aldolase family that catalyzes the cleavage of d-fructose 1,6-bisphosphate (FBP) into dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) and d-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P). In addition to the active site zinc, the catalytic apparatus of FBPA employs an aspartic acid, Asp83 in the G. lamblia enzyme, which when replaced with an alanine residue renders the enzyme inactive. A comparison of the crystal structures of D83A FBPA in complex with FBP and of wild-type FBPA in the unbound state revealed a substrate-induced conformational transition of loops in the vicinity of the active site and a shift in the location of Zn(2+). When FBP binds, the Zn(2+) shifts up to 4.6 A toward the catalytic Asp83, which brings the metal within coordination distance of the Asp83 carboxylate group. In addition, the structure of wild-type FBPA was determined in complex with the competitive inhibitor d-tagatose 1,6-bisphosphate (TBP), a FBP stereoisomer. In this structure, the zinc binds in a site close to that previously seen in the structure of FBPA in complex with phosphoglycolohydroxamate, an analogue of the postulated DHAP ene-diolate intermediate. Together, the ensemble of structures suggests that the zinc mobility is necessary to orient the Asp83 side chain and to polarize the substrate for proton transfer from the FBP C(4) hydroxyl group to the Asp83 carboxyl group. In the absence of FBP, the alternative zinc position is too remote for coordinating the Asp83. We propose a modification of the catalytic mechanism that incorporates the novel features observed in the FBPA-FBP structure. The mechanism invokes coordination and coplanarity of the Zn(2+) with the FBP's O-C(3)-C(4)-O group concomitant with coordination of the Asp83 carboxylic group. Catalysis is accompanied by movement of Zn(2+) to a site coplanar with the O-C(2)-C(3)-O group of the DHAP. glFBPA exhibits strict substrate specificity toward FBP and does not cleave TBP. The active sites of FBPAs contain an aspartate residue equivalent to Asp255 of glFBPA, whereas tagatose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase contains an alanine in this position. We and others hypothesized that this aspartic acid is a likely determinant of FBP versus TBP specificity. Replacement of Asp255 with an alanine resulted in an enzyme that possesses double specificity, now cleaving TBP (albeit with low efficacy; k(cat)/K(m) = 80 M(-1) s(-1)) while maintaining activity toward FBP at a 50-fold lower catalytic efficacy compared with that of wild-type FBPA. The collection of structures and sequence analyses highlighted additional residues that may be involved in substrate discrimination.
Figures



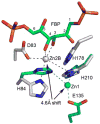


References
-
- Kobes RD, Simpson RT, Vallee RL, Rutter WJ. A functional role of metal ions in a class II aldolase. Biochemistry. 1969;8:585–588. - PubMed
-
- Rutter WJ. Evolution of Aldolase. Fed Proc. 1964;23:1248–1257. - PubMed
-
- Blom NS, Tetreault S, Coulombe R, Sygusch J. Novel active site in Escherichia coli fructose 1,6-bisphosphate aldolase. Nat Struct Biol. 1996;3:856–862. - PubMed
-
- Cooper SJ, Leonard GA, McSweeney SM, Thompson AW, Naismith JH, Qamar S, Plater A, Berry A, Hunter WN. The crystal structure of a class II fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase shows a novel binuclear metal-binding active site embedded in a familiar fold. Structure. 1996;4:1303–1315. - PubMed
-
- Hall DR, Leonard GA, Reed CD, Watt CI, Berry A, Hunter WN. The crystal structure of Escherichia coli class II fructose-1, 6-bisphosphate aldolase in complex with phosphoglycolohydroxamate reveals details of mechanism and specificity. J Mol Biol. 1999;287:383–394. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

