Changes in cerebral blood flow after acetazolamide: an experimental study comparing near-infrared spectroscopy and SPECT
- PMID: 19236469
- PMCID: PMC2782727
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1468-1331.2008.02398.x
Changes in cerebral blood flow after acetazolamide: an experimental study comparing near-infrared spectroscopy and SPECT
Abstract
Background and purpose: It is important to find a reliable and bedside method, which can estimate the cerebral blood flow (CBF) of patients in clinical settings. Estimation of CBF by calculating a blood flow index (BFI) using continuous wave near-infrared spectroscopy (CW-NIRS) and indocyanine green (ICG) as an i.v. tracer has been proposed to be a feasible and promising method. To validate if the BFI method can detect relative changes in CBF we compared data with the established method (133)Xenon single photon emission computer tomography ((133)Xe-SPECT).
Methods: Ten healthy subjects were investigated before and after a bolus of acetazolamide. NIRS data were obtained using a multi source detector separation configuration in order to assess a corrected BFI (BFI(corr)) value, which attempts to eliminate contamination of skin blood flow.
Results: Data obtained showed no significant correlation between CBF changes measured by (133)Xe-SPECT and BFI(corr) (0.133, P = 0.732). After acetazolamide, a 49% increase in CBF was detected using the (133)Xe-SPECT method, whereas no changes in any ICG variables were observed after acetazolamide.
Conclusion: The study shows that it is not possible to obtain reliable BFI data, which reflect changes in CBF after acetazolamide infusion, using the CW-NIRS and ICG method.
Figures

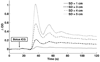
 ) after infusion of acetazolamide. A significant increase in CBFMCA was found 15 min (48.9 ± 6.6, *** P < 0.001) and 60 min (26.0 ± 6.8, ** P = 0.003) after acetazolamide bolus.
) after infusion of acetazolamide. A significant increase in CBFMCA was found 15 min (48.9 ± 6.6, *** P < 0.001) and 60 min (26.0 ± 6.8, ** P = 0.003) after acetazolamide bolus.


References
-
- Damian MS, Schlosser R. Bilateral near infrared spectroscopy in space-occupying middle cerebral artery stroke. Neurocritical Care. 2007;6:165–173. - PubMed
-
- Al-Rawi PG. Near infrared spectroscopy in brain injury: today’s perspective. Acta Neurochirurgica. Supplement. 2005;95:453–457. - PubMed
-
- Haitsma IK, Maas AI. Monitoring cerebral oxygenation in traumatic brain injury. Progress in Brain Research. 2007;161:207–216. - PubMed
-
- Strangman G, Boas DA, Sutton JP. Non-invasive neuroimaging using near-infrared light. Biological Psychiatry. 2002;52:679–693. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

