Effects of aging on the immunopathologic response to sepsis
- PMID: 19237912
- PMCID: PMC2760736
- DOI: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e3181968f3a
Effects of aging on the immunopathologic response to sepsis
Abstract
Objective: Aging is associated with increased inflammation following sepsis. The purpose of this study was to determine whether this represents a fundamental age-based difference in the host response or is secondary to the increased mortality seen in aged hosts.
Design: Prospective, randomized controlled study.
Setting: Animal laboratory in a university medical center.
Subjects: Young (6-12 weeks) and aged (20-24 months) FVB/N mice.
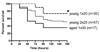
Interventions: Mice were subjected to 2 x 25 or 1 x 30 cecal ligation and puncture (CLP).
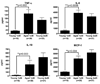
Measurements and main results: Survival was similar in young mice subjected to 2 x 25 CLP and aged mice subjected to 1 x 30 CLP (p = 0.15). Young mice subjected to 1 x 30 CLP had improved survival compared with the other groups (p < 0.05). When injury was held constant but mortality was greater, both systemic and peritoneal levels of tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin (IL)-6, IL-10, and monocyte chemotactic protein-1 were elevated 24 hours after CLP in aged animals compared with young animals (p < 0.05). When mortality was similar but injury severity was different, there were no significant differences in systemic cytokines between aged mice and young mice. In contrast, peritoneal levels of tumor necrosis factor-alpha, IL-6, and IL-10 were higher in aged mice subjected to 1 x 30 CLP than young mice subjected to 2 x 25 CLP despite their similar mortalities (p < 0.05). There were no significant differences in either bacteremia or peritoneal cultures when animals of different ages sustained similar injuries or had different injuries with similar mortalities.
Conclusions: Aged mice are more likely to die of sepsis than young mice when subjected to an equivalent insult, and this is associated with increases in both systemic and local inflammation. There is an exaggerated local but not systemic inflammatory response in aged mice compared with young mice when mortality is similar. This suggests that systemic processes that culminate in death may be age independent, but the local inflammatory response may be greater with aging.
Figures



References
-
- Angus DC, Linde-Zwirble WT, Lidicker J, et al. Epidemiology of severe sepsis in the United States: analysis of incidence, outcome, and associated costs of care. Crit Care Med. 2001;29:1303–1310. - PubMed
-
- Martin GS, Mannino DM, Moss M. The effect of age on the development and outcome of adult sepsis. Crit Care Med. 2006;34:15–21. - PubMed
-
- Martin GS, Mannino DM, Eaton S, et al. The epidemiology of sepsis in the United States from 1979 through 2000. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1546–1554. - PubMed
-
- Turnbull IR, Wlzorek JJ, Osborne D, et al. Effects of age on mortality and antibiotic efficacy in cecal ligation and puncture. Shock. 2003;19:310–313. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

