Sex dependent effects of perinatal taurine exposure on the arterial pressure control in adult offspring
- PMID: 19239144
- PMCID: PMC2672946
- DOI: 10.1007/978-0-387-75681-3_14
Sex dependent effects of perinatal taurine exposure on the arterial pressure control in adult offspring
Abstract
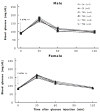
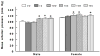
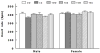
The present study tests the sex-dependent effect of perinatal taurine exposure on arterial pressure control in adults. Female Sprague-Dawley rats were fed normal rat chow with 3% beta-alanine (taurine depletion,TD), 3% taurine (taurine supplementation,TS) or water alone (C) from conception to weaning. Their male and female offspring were then fed normal rat chow and tap water with 5% glucose (C with glucose, CG; TD with glucose, TDG; TS with glucose, TSG) or water alone (CW, TDW or TSW). At 7-8 weeks of age, they were studied in a conscious condition. Body weights were lower in male and female TDG and male TDW rats. Kidney to body weights increased in female TSW but not TSG. Plasma sodium and potassium were not significantly different among males. Among females, plasma sodium levels were lower in all glucose treated groups while plasma potassium levels were lower only in TDG. Hematocrit, fasting blood glucose, and glucose tolerance were not significantly different between the sexes. Mean arterial pressure increased in male TDG, TSW, and TSG while in the females, mean arterial pressure increased in TabstractDW, TDG, and TSG. Heart rates were not significantly different between the sexes. The present data indicate that perinatal taurine exposure alters arterial pressure control of adult rats and this effect is gender specific.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Perinatal taurine exposure alters renal potassium excretion mechanisms in adult conscious rats.J Biomed Sci. 2010 Aug 24;17 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S29. doi: 10.1186/1423-0127-17-S1-S29. J Biomed Sci. 2010. PMID: 20804604 Free PMC article.
-
Perinatal Taurine Imbalance Followed by High Sugar Intake Alters the Effects of Estrogen on Renal Excretory Function in Adult Female Rats.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;975 Pt 2:769-787. doi: 10.1007/978-94-024-1079-2_60. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 28849498
-
Perinatal taurine alters arterial pressure control and renal function in adult offspring.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2009;643:145-56. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-75681-3_15. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2009. PMID: 19239145 Free PMC article.
-
Perinatal taurine exposure affects adult oxidative stress.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2013 Jul 15;305(2):R95-7. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00142.2013. Epub 2013 Apr 24. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23616107 Review.
-
NIEHS Report on the Toxicity Studies of Nicotine Bitartrate Dihydrate (CASRN 6019-06-3) Administered in Drinking Water to Sprague Dawley Rats and Swiss Mice: NIEHS Report 11 [Internet].Research Triangle Park (NC): National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences; 2024 Oct. Research Triangle Park (NC): National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences; 2024 Oct. PMID: 39441944 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Taurine and the renal system.J Biomed Sci. 2010 Aug 24;17 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S4. doi: 10.1186/1423-0127-17-S1-S4. J Biomed Sci. 2010. PMID: 20804616 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Perinatal taurine exposure alters renal potassium excretion mechanisms in adult conscious rats.J Biomed Sci. 2010 Aug 24;17 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S29. doi: 10.1186/1423-0127-17-S1-S29. J Biomed Sci. 2010. PMID: 20804604 Free PMC article.
-
Perinatal taurine exposure affects adult arterial pressure control.Amino Acids. 2014 Jan;46(1):57-72. doi: 10.1007/s00726-012-1417-5. Epub 2012 Oct 16. Amino Acids. 2014. PMID: 23070226 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Perinatal Taurine Supplementation Alters Renal Function via Renin-Angiotensin System Overactivity in Adult Female Rats.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;975 Pt 2:757-768. doi: 10.1007/978-94-024-1079-2_59. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 28849497
-
Perinatal Taurine Supplementation Prevents Metabolic and Cardiovascular Effects of Maternal Diabetes in Adult Rat Offspring.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;975 Pt 1:295-305. doi: 10.1007/978-94-024-1079-2_26. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 28849464
References
-
- Aerts L, Van Assche FA. Taurine and taurine-deficiency in the perinatal period. J Perinat Med. 2002;30:281–6. - PubMed
-
- Anuradha CV, Balakrishnan SD. Taurine attenuates hypertension and improves insulin sensitivity in the fructose-fed rat, an animal model of insulin resistance. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1999;77:749–54. - PubMed
-
- Ashraf MS, Vongpatanasin W. Estrogen and hypertension. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2006;8:368–76. - PubMed
-
- Azuma M, Takahashi K, Fukuda T, Ohyabu Y, Yamamoto I, Kim S, Iwao H, Schaffer SW, Azuma J. Taurine attenuates hypertrophy induced by angiotensin II in cultured neonatal rat cardiac myocytes. Eur J Pharmacol. 2000;403:181–8. - PubMed
-
- Barker DJ. The origins of the developmental origins theory. J Intern Med. 2007;261:412–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

