RNA and disease
- PMID: 19239895
- PMCID: PMC2866189
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.02.011
RNA and disease
Abstract
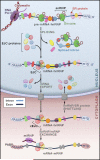
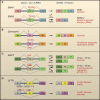
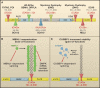
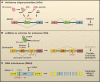
Cellular functions depend on numerous protein-coding and noncoding RNAs and the RNA-binding proteins associated with them, which form ribonucleoprotein complexes (RNPs). Mutations that disrupt either the RNA or protein components of RNPs or the factors required for their assembly can be deleterious. Alternative splicing provides cells with an exquisite capacity to fine-tune their transcriptome and proteome in response to cues. Splicing depends on a complex code, numerous RNA-binding proteins, and an enormously intricate network of interactions among them, increasing the opportunity for exposure to mutations and misregulation that cause disease. The discovery of disease-causing mutations in RNAs is yielding a wealth of new therapeutic targets, and the growing understanding of RNA biology and chemistry is providing new RNA-based tools for developing therapeutics.
Figures
References
-
- Alter J, Lou F, Rabinowitz A, Yin H, Rosenfeld J, Wilton SD, Partridge TA, Lu QL. Systemic delivery of morpholino oligonucleotide restores dystrophin expression bodywide and improves dystrophic pathology. Nat Med. 2006;12:175–177. - PubMed
-
- Asparuhova MB, Marti G, Liu S, Serhan F, Trono D, Schumperli D. Inhibition of HIV-1 multiplication by a modified U7 snRNA inducing Tat and Rev exon skipping. J Gene Med. 2007;9:323–334. - PubMed
-
- Barreau C, Paillard L, Mereau A, Osborne HB. Mammalian CELF/Bruno-like RNA-binding proteins: molecular characteristics and biological functions. Biochimie. 2006;88:515–525. - PubMed
-
- Bhalla K, Phillips HA, Crawford J, McKenzie OL, Mulley JC, Eyre H, Gardner AE, Kremmidiotis G, Callen DF. The de novo chromosome 16 translocations of two patients with abnormal phenotypes (mental retardation and epilepsy) disrupt the A2BP1 gene. J Hum Genet. 2004;49:308–311. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

