Maintaining a stochastic neuronal cell fate decision
- PMID: 19240127
- PMCID: PMC3959998
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1780509
Maintaining a stochastic neuronal cell fate decision
Abstract
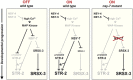
Sensory systems generally contain a number of neuronal subtypes that express distinct sensory receptor proteins. This diversity is generated through deterministic and stochastic cell fate choices, while maintaining the subtype often requires a distinct mechanism. In a study published in the February 1, 2009, issue of Genes & Development, Lesch and colleagues (pp. 345-358) describe a new transcription factor, NSY-7, that acts to stabilize a stochastic subtype choice in AWC chemosensory neurons in Caenorhabditis elegans.
Figures
Comment on
-
Transcriptional regulation and stabilization of left-right neuronal identity in C. elegans.Genes Dev. 2009 Feb 1;23(3):345-58. doi: 10.1101/gad.1763509. Genes Dev. 2009. PMID: 19204119 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Transcriptional regulation and stabilization of left-right neuronal identity in C. elegans.Genes Dev. 2009 Feb 1;23(3):345-58. doi: 10.1101/gad.1763509. Genes Dev. 2009. PMID: 19204119 Free PMC article.
-
The microRNA mir-71 inhibits calcium signaling by targeting the TIR-1/Sarm1 adaptor protein to control stochastic L/R neuronal asymmetry in C. elegans.PLoS Genet. 2012;8(8):e1002864. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002864. Epub 2012 Aug 2. PLoS Genet. 2012. PMID: 22876200 Free PMC article.
-
A universal transportin protein drives stochastic choice of olfactory neurons via specific nuclear import of a sox-2-activating factor.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Dec 10;116(50):25137-25146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1908168116. Epub 2019 Nov 25. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 31767767 Free PMC article.
-
Securing Neuronal Cell Fate in C. elegans.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2016;116:167-80. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctdb.2015.11.011. Epub 2016 Jan 23. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2016. PMID: 26970619 Review.
-
Stochastic left-right neuronal asymmetry in Caenorhabditis elegans.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2016 Dec 19;371(1710):20150407. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2015.0407. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27821536 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hierarchical deployment of Tbx3 dictates the identity of hypothalamic KNDy neurons to control puberty onset.Sci Adv. 2022 Nov 18;8(46):eabq2987. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abq2987. Epub 2022 Nov 16. Sci Adv. 2022. PMID: 36383654 Free PMC article.
-
Natural variation in stochastic photoreceptor specification and color preference in Drosophila.Elife. 2017 Dec 18;6:e29593. doi: 10.7554/eLife.29593. Elife. 2017. PMID: 29251595 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional repression in stochastic gene expression, patterning, and cell fate specification.Dev Biol. 2022 Jan;481:129-138. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2021.10.002. Epub 2021 Oct 21. Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 34688689 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bargmann C.I., Hartwieg E., Horvitz H.R. Odorant-selective genes and neurons mediate olfaction in C. elegans. Cell. 1993;74:515–527. - PubMed
-
- Bauer Huang S.L., Saheki Y., VanHoven M.K., Torayama I., Ishihara T., Katsura I., van der Linden A., Sengupta P., Bargmann C.I. Left–right olfactory asymmetry results from antagonistic functions of voltage-activated calcium channels and the Raw repeat protein OLRN-1 in C. elegans. Neural Develop. 2007;2:24. doi: 10.1186/1749-8104-2-24. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chess A., Buck L., Dowling M.M., Axel R., Ngai J. Molecular biology of smell: Expression of the multigene family encoding putative odorant receptors. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 1992;57:505–516. - PubMed
-
- Chuang C.F., Vanhoven M.K., Fetter R.D., Verselis V.K., Bargmann C.I. An innexin-dependent cell network establishes left–right neuronal asymmetry in C. elegans. Cell. 2007;129:787–799. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous