Regulation of leukemic cell differentiation and retinoid-induced gene expression by statins
- PMID: 19240159
- PMCID: PMC2681262
- DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-08-1196
Regulation of leukemic cell differentiation and retinoid-induced gene expression by statins
Abstract
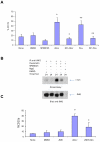
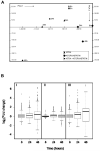
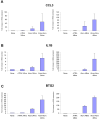
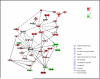
There is emerging evidence that, beyond their cholesterol-lowering properties, statins exhibit important antileukemic effects in vitro and in vivo, but the precise mechanisms by which they generate such responses remain to be determined. We have previously shown that statins promote differentiation of acute promyelocytic leukemia cells and enhance generation of all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA)-dependent antileukemic responses. We now provide evidence that statin-dependent leukemic cell differentiation requires engagement and activation of the c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase kinase pathway. In addition, in experiments, to define the molecular targets and mediators of statin-induced differentiation, we found a remarkable effect of statins on ATRA-dependent gene transcription, evidenced by the selective induction of over 400 genes by the combination of atorvastatin and ATRA. Altogether, our studies identify novel statin molecular targets linked to differentiation, establish that statins modulate ATRA-dependent transcription, and suggest that combined use of statins with retinoids may provide a novel approach to enhance antileukemic responses in acute promyelocytic leukemia and possibly other leukemias.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Statin-dependent activation of protein kinase Cδ in acute promyelocytic leukemia cells and induction of leukemic cell differentiation.Leuk Lymphoma. 2012 Sep;53(9):1779-84. doi: 10.3109/10428194.2012.668287. Epub 2012 Apr 19. Leuk Lymphoma. 2012. PMID: 22356114 Free PMC article.
-
Suppressive effects of statins on acute promyelocytic leukemia cells.Cancer Res. 2007 May 1;67(9):4524-32. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-3686. Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17483369
-
Effects of novel retinoid X receptor-selective ligands on myeloid leukemia differentiation and proliferation in vitro.Blood. 1996 Mar 1;87(5):1977-84. Blood. 1996. PMID: 8634447
-
Effects of novel RAR- and RXR-selective retinoids on myeloid leukemic proliferation and differentiation in vitro.Blood. 1999 Mar 15;93(6):2057-66. Blood. 1999. PMID: 10068679
-
Mechanisms of all-trans retinoic acid-induced differentiation of acute promyelocytic leukemia cells.J Biosci. 2000 Sep;25(3):275-84. doi: 10.1007/BF02703936. J Biosci. 2000. PMID: 11022230 Review.
Cited by
-
Simvastatin modulates mesenchymal stromal cell proliferation and gene expression.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 13;10(4):e0120137. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0120137. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25874574 Free PMC article.
-
Interferon regulatory factor-1 binds c-Cbl, enhances mitogen activated protein kinase signaling and promotes retinoic acid-induced differentiation of HL-60 human myelo-monoblastic leukemia cells.Leuk Lymphoma. 2011 Dec;52(12):2372-9. doi: 10.3109/10428194.2011.603449. Epub 2011 Aug 24. Leuk Lymphoma. 2011. PMID: 21740303 Free PMC article.
-
Hypomethylating agents induce epigenetic and transcriptional heterogeneity with implications for acute myeloid leukemia cell self-renewal.Leukemia. 2025 Sep;39(9):2275-2280. doi: 10.1038/s41375-025-02693-5. Epub 2025 Jul 17. Leukemia. 2025. PMID: 40676205 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Regulation of the kinase RSK1 by arsenic trioxide and generation of antileukemic responses.Cancer Biol Ther. 2013 May;14(5):411-6. doi: 10.4161/cbt.23760. Epub 2013 Feb 1. Cancer Biol Ther. 2013. PMID: 23377826 Free PMC article.
-
Statin-dependent activation of protein kinase Cδ in acute promyelocytic leukemia cells and induction of leukemic cell differentiation.Leuk Lymphoma. 2012 Sep;53(9):1779-84. doi: 10.3109/10428194.2012.668287. Epub 2012 Apr 19. Leuk Lymphoma. 2012. PMID: 22356114 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Goldstein JL, Brown MS. Regulation of the mevalonate pathway. Nature. 1990;343:425–30. - PubMed
-
- Istvan ES, Deisenhofer J. Structural mechanism for statin inhibition of HMG-CoA reductase. Science. 2001;292:1160–64. - PubMed
-
- Ness GC, Zhao Z, Lopez D. Inhibitors of cholesterol biosynthesis increase hepatic low-density lipoprotein receptor protein degradation. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1996;325:242–48. - PubMed
-
- Sacks FM, Pfeffer MA, Moye LA, et al. Cholesterol and recurrent Events Trial investigators. The effect of pravastatin on coronary events after myocardial infarction in patients with average cholesterol levels. N Engl J Med. 1996;335:1001–9. - PubMed
-
- The long-term intervention with pravastatin in ischaemic disease (LIPID) study group Prevention of cardiovascular events and death with pravastatin in patients with coronary heart disease and a broad range of initial cholesterol levels. N Engl J Med. 1998;339:1349–57. No Authors Listed. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

