Cytosolic phospholipase A2: targeting cancer through the tumor vasculature
- PMID: 19240173
- PMCID: PMC2874582
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-1905
Cytosolic phospholipase A2: targeting cancer through the tumor vasculature
Abstract
Purpose: In vascular endothelial cells, low doses of ionizing radiation trigger the immediate activation of cytosolic phospholipase A2 (cPLA2). This event initiates prosurvival signaling that could be responsible for radioresistance of tumor vasculature. Thus, the development of radiosensitizers targeting these survival pathways may enhance tumor response to radiation therapy. Arachidonyltrifluoromethyl Ketone (AACOCF3), a specific cPLA2 inhibitor, was studied as a potential radiosensitizer.
Experimental design: Vascular endothelial cells (3B11 and MPMEC) and lung tumor cells (LLC and H460) were treated with 1 micromol/L AACOCF3 for 30 minutes prior to irradiation. Treatment response was evaluated by clonogenic survival, activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2), tubule formation, and migration assays. For in vivo experiments, mice with LLC or H460 tumors in the hind limbs were treated for 5 consecutive days with 10 mg/kg AACOCF3 administered daily 30 minutes prior to irradiation. Treatment response was assessed by tumor growth delay, Power Doppler Sonography, and immunohistochemistry.
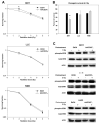
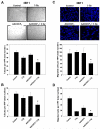
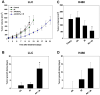
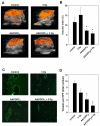
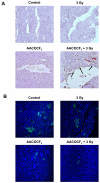
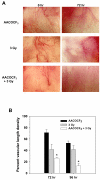
Results: In cell culture experiments, inhibition of cPLA2 with AACOCF3 prevented radiation-induced activation of ERK1/2 and decreased clonogenic survival of irradiated vascular endothelial cells but not the lung tumor cells. Treatment with AACOCF3 also attenuated tubule formation and migration in irradiated vascular endothelial cells. In both tumor mouse models, treatment with AACOCF3 prior to irradiation significantly suppressed tumor growth and decreased overall tumor blood flow and vascularity. Increased apoptosis in both tumor cells and tumor vascular endothelium was determined as a possible mechanism of the observed effect.
Conclusion: These findings identify cPLA2 as a novel molecular target for tumor sensitization to radiation therapy through the tumor vasculature.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cytosolic phospholipase A2 and lysophospholipids in tumor angiogenesis.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2010 Sep 22;102(18):1398-412. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djq290. Epub 2010 Aug 20. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2010. PMID: 20729478 Free PMC article.
-
Cytosolic phospholipaseA2 inhibition with PLA-695 radiosensitizes tumors in lung cancer animal models.PLoS One. 2013 Jul 19;8(7):e69688. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0069688. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23894523 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting tumor angiogenesis with histone deacetylase inhibitors: the hydroxamic acid derivative LBH589.Clin Cancer Res. 2006 Jan 15;12(2):634-42. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-1132. Clin Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 16428510
-
A specific antagonist of the p110delta catalytic component of phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase, IC486068, enhances radiation-induced tumor vascular destruction.Cancer Res. 2004 Jul 15;64(14):4893-9. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-03-3955. Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 15256460
-
Broad spectrum receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, SU6668, sensitizes radiation via targeting survival pathway of vascular endothelium.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004 Mar 1;58(3):844-50. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2003.10.049. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004. PMID: 14967441
Cited by
-
cPLA2 blockade attenuates S100A7-mediated breast tumorigenicity by inhibiting the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022 Feb 8;41(1):54. doi: 10.1186/s13046-021-02221-0. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35135586 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor-Endothelial Cell Three-dimensional Spheroids: New Aspects to Enhance Radiation and Drug Therapeutics.Transl Oncol. 2011 Dec;4(6):365-76. doi: 10.1593/tlo.11187. Epub 2011 Dec 1. Transl Oncol. 2011. PMID: 22191001 Free PMC article.
-
Cytosolic phospholipase A2 and lysophospholipids in tumor angiogenesis.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2010 Sep 22;102(18):1398-412. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djq290. Epub 2010 Aug 20. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2010. PMID: 20729478 Free PMC article.
-
A VE-cadherin-PAR3-α-catenin complex regulates the Golgi localization and activity of cytosolic phospholipase A(2)α in endothelial cells.Mol Biol Cell. 2012 May;23(9):1783-96. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E11-08-0694. Epub 2012 Mar 7. Mol Biol Cell. 2012. PMID: 22398721 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the eicosanoid pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma.Am J Cancer Res. 2021 Jun 15;11(6):2456-2476. eCollection 2021. Am J Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 34249410 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wagner H., Jr. Postoperative adjuvant therapy for patients with resected non-small cell lung cancer: still controversial after all these years. Chest. 2000;117:110S–8S. - PubMed
-
- Lee JH, Machtay M, Kaiser LR, et al. Non-small cell lung cancer: prognostic factors in patients treated with surgery and postoperative radiation therapy. Radiology. 1999;213:845–52. - PubMed
-
- Clamon G, Herndon J, Cooper R, Chang AY, Rosenman J, Green MR. Radiosensitization with carboplatin for patients with unresectable stage III non-small-cell lung cancer: a phase III trial of the Cancer and Leukemia Group B and the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17:4–11. - PubMed
-
- Dietz A, Boehm A, Mozet C, Wichmann G, Giannis A. Current aspects of targeted therapy in head and neck tumors. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2008 - PubMed
-
- Forastiere AA, Trotti A, Pfister DG, Grandis JR. Head and neck cancer: recent advances and new standards of care. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2006;24:2603–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 CA125757/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-CA125757/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21-CA128456/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 CA128456/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-CA088076/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA140220/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA090949/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA088076/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA089674/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA112385/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 2R01-CA089674/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50-CA090949/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-CA112385/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

