Ubiquitin-binding motif of human DNA polymerase eta is required for correct localization
- PMID: 19240217
- PMCID: PMC2650340
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0812744106
Ubiquitin-binding motif of human DNA polymerase eta is required for correct localization
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
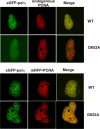
Comment on
-
Roles of PCNA-binding and ubiquitin-binding domains in human DNA polymerase eta in translesion DNA synthesis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Nov 18;105(46):17724-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0809844105. Epub 2008 Nov 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 19001268 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bienko M, et al. Ubiquitin-binding domains in translesion synthesis polymerases. Science. 2005;310:1821–1824. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

