Engineering clustered ligand binding into nonviral vectors: alphavbeta3 targeting as an example
- PMID: 19240693
- PMCID: PMC2835129
- DOI: 10.1038/mt.2009.11
Engineering clustered ligand binding into nonviral vectors: alphavbeta3 targeting as an example
Abstract
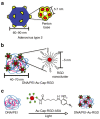
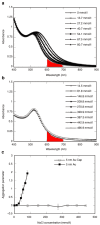
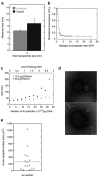
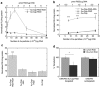
The development of techniques to efficiently deliver genes using nonviral approaches can broaden the application of gene delivery in medical applications without the safety concerns associated with viral vectors. Here, we designed a clustered integrin-binding platform to enhance the efficiency and targetability of nonviral gene transfer to HeLa cells with low and high densities of alpha(v)beta(3) integrin receptors. Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD) nanoclusters were formed using gold nanoparticles functionalized with RGD peptides and used to modify the surface of DNA/poly(ethylene imine) (PEI) polyplexes. DNA/PEI polyplexes with attached RGD nanoclusters resulted in either 5.4- or 35-fold increase in gene transfer efficiency over unmodified polyplexes for HeLa cells with low- or high-integrin surface density, respectively. The transfection efficiency obtained with the commercially available vector jetPEI-RGD was used for comparison as a vector without clustered binding. JetPEI-RGD exhibited a 1.2-fold enhancement compared to unmodified jetPEI in cells with high densities of alpha(v)beta(3) integrin receptors. The data presented here emphasize the importance of the RGD conformational arrangement on the surface of the polyplex to achieve efficient targeting and gene transfer, and provide an approach to introduce clustering to a wide variety of nanoparticles for gene delivery.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Integrin targeting using RGD-PEI conjugates for in vitro gene transfer.J Gene Med. 2003 Jul;5(7):588-99. doi: 10.1002/jgm.382. J Gene Med. 2003. PMID: 12825198
-
Integrin alphaVbeta3 targeted gene delivery using RGD peptidomimetic conjugates with copolymers of PEGylated poly(ethylene imine).Bioconjug Chem. 2009 Jun;20(6):1270-80. doi: 10.1021/bc9001695. Bioconjug Chem. 2009. PMID: 19476331
-
Self-assembled nanofibrils from RGD-functionalized cellulose nanocrystals to improve the performance of PEI/DNA polyplexes.J Colloid Interface Sci. 2019 Oct 1;553:71-82. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2019.06.001. Epub 2019 Jun 3. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2019. PMID: 31200231
-
Clustering and internalization of integrin alphavbeta3 with a tetrameric RGD-synthetic peptide.Mol Ther. 2009 May;17(5):837-43. doi: 10.1038/mt.2009.29. Epub 2009 Mar 3. Mol Ther. 2009. PMID: 19259068 Free PMC article.
-
RGD peptide-based non-viral gene delivery vectors targeting integrin αvβ3 for cancer therapy.J Drug Target. 2019 Jan;27(1):1-11. doi: 10.1080/1061186X.2018.1455841. Epub 2018 Apr 6. J Drug Target. 2019. PMID: 29564914 Review.
Cited by
-
Non-viral Delivery of Nucleic Acids: Insight Into Mechanisms of Overcoming Intracellular Barriers.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Aug 21;9:971. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00971. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30186185 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endothelial cell-targeted pVEGF165 polyplex plays a pivotal role in inhibiting intimal thickening after vascular injury.Int J Nanomedicine. 2015 Sep 10;10:5751-68. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S88109. eCollection 2015. Int J Nanomedicine. 2015. PMID: 26425083 Free PMC article.
-
Gene delivery by peptide-assisted transport.Curr Opin Biomed Eng. 2018 Sep;7:71-82. doi: 10.1016/j.cobme.2018.10.002. Epub 2018 Oct 9. Curr Opin Biomed Eng. 2018. PMID: 30906908 Free PMC article.
-
Clustered Arg-Gly-Asp peptides enhances tumor targeting of nonviral vectors.ChemMedChem. 2011 Apr 4;6(4):623-7. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.201000541. Epub 2011 Jan 24. ChemMedChem. 2011. PMID: 21442757 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Microdistribution of MC1R-targeted polyplexes in murine melanoma tumor tissue.Biomaterials. 2013 Dec;34(38):10209-16. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.08.076. Epub 2013 Sep 27. Biomaterials. 2013. PMID: 24075405 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arnold M, Cavalcanti-Adam EA, Glass R, Blummel J, Eck W, Kantlehner M, et al. Activation of integrin function by nanopatterned adhesive interfaces. Chemphyschem. 2004;5:383–388. - PubMed
-
- Koo LY, Irvine DJ, Mayes AM, Lauffenburger DA., and , Griffith LG. Co-regulation of cell adhesion by nanoscale RGD organization and mechanical stimulus. J Cell Sci. 2002;115:1423–1433. - PubMed
-
- Maheshwari G, Brown G, Lauffenburger DA, Wells A., and , Griffith LG. Cell adhesion and motility depend on nanoscale RGD clustering. J Cell Sci. 2000;113:1677–1686. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

