Engineering clustered ligand binding into nonviral vectors: alphavbeta3 targeting as an example
- PMID: 19240693
- PMCID: PMC2835129
- DOI: 10.1038/mt.2009.11
Engineering clustered ligand binding into nonviral vectors: alphavbeta3 targeting as an example
Abstract
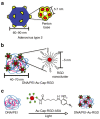
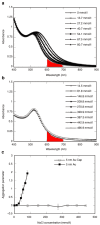
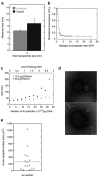
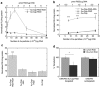
The development of techniques to efficiently deliver genes using nonviral approaches can broaden the application of gene delivery in medical applications without the safety concerns associated with viral vectors. Here, we designed a clustered integrin-binding platform to enhance the efficiency and targetability of nonviral gene transfer to HeLa cells with low and high densities of alpha(v)beta(3) integrin receptors. Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD) nanoclusters were formed using gold nanoparticles functionalized with RGD peptides and used to modify the surface of DNA/poly(ethylene imine) (PEI) polyplexes. DNA/PEI polyplexes with attached RGD nanoclusters resulted in either 5.4- or 35-fold increase in gene transfer efficiency over unmodified polyplexes for HeLa cells with low- or high-integrin surface density, respectively. The transfection efficiency obtained with the commercially available vector jetPEI-RGD was used for comparison as a vector without clustered binding. JetPEI-RGD exhibited a 1.2-fold enhancement compared to unmodified jetPEI in cells with high densities of alpha(v)beta(3) integrin receptors. The data presented here emphasize the importance of the RGD conformational arrangement on the surface of the polyplex to achieve efficient targeting and gene transfer, and provide an approach to introduce clustering to a wide variety of nanoparticles for gene delivery.
Figures



References
-
- Arnold M, Cavalcanti-Adam EA, Glass R, Blummel J, Eck W, Kantlehner M, et al. Activation of integrin function by nanopatterned adhesive interfaces. Chemphyschem. 2004;5:383–388. - PubMed
-
- Koo LY, Irvine DJ, Mayes AM, Lauffenburger DA., and , Griffith LG. Co-regulation of cell adhesion by nanoscale RGD organization and mechanical stimulus. J Cell Sci. 2002;115:1423–1433. - PubMed
-
- Maheshwari G, Brown G, Lauffenburger DA, Wells A., and , Griffith LG. Cell adhesion and motility depend on nanoscale RGD clustering. J Cell Sci. 2000;113:1677–1686. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

