Identification of thyroid hormone receptor binding sites and target genes using ChIP-on-chip in developing mouse cerebellum
- PMID: 19240802
- PMCID: PMC2643481
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0004610
Identification of thyroid hormone receptor binding sites and target genes using ChIP-on-chip in developing mouse cerebellum
Abstract
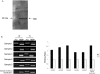
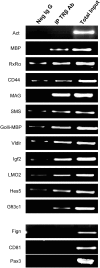
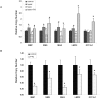
Thyroid hormone (TH) is critical to normal brain development, but the mechanisms operating in this process are poorly understood. We used chromatin immunoprecipitation to enrich regions of DNA bound to thyroid receptor beta (TRbeta) of mouse cerebellum sampled on post natal day 15. Enriched target was hybridized to promoter microarrays (ChIP-on-chip) spanning -8 kb to +2 kb of the transcription start site (TSS) of 5000 genes. We identified 91 genes with TR binding sites. Roughly half of the sites were located in introns, while 30% were located within 1 kb upstream (5') of the TSS. Of these genes, 83 with known function included genes involved in apoptosis, neurodevelopment, metabolism and signal transduction. Two genes, MBP and CD44, are known to contain TREs, providing validation of the system. This is the first report of TR binding for 81 of these genes. ChIP-on-chip results were confirmed for 10 of the 13 binding fragments using ChIP-PCR. The expression of 4 novel TH target genes was found to be correlated with TH levels in hyper/hypothyroid animals providing further support for TR binding. A TRbeta binding site upstream of the coding region of myelin associated glycoprotein was demonstrated to be TH-responsive using a luciferase expression system. Motif searches did not identify any classic binding elements, indicating that not all TR binding sites conform to variations of the classic form. These findings provide mechanistic insight into impaired neurodevelopment resulting from TH deficiency and a rich bioinformatics resource for developing a better understanding of TR binding.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
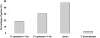

References
-
- Bernal J. Thyroid hormone receptors in brain development and function. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab. 2007;3:249–259. - PubMed
-
- Zoeller RT, Rovet J. Timing of thyroid hormone action in the developing brain: clinical observations and experimental findings. J Neuroendocrinol. 2004;16:809–818. - PubMed
-
- Delange F. Neonatal screening for congenital hypothyroidism: results and perspectives. Horm Res. 1997;48:51–61. - PubMed
-
- Harris KB, Pass KA. Increase in congenital hypothyroidism in New York State and in the United States. Mol Genet Metab. 2007;91:268–277. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

