Lone pair ... pi interactions between water oxygens and aromatic residues: quantum chemical studies based on high-resolution protein structures and model compounds
- PMID: 19241386
- PMCID: PMC2760365
- DOI: 10.1002/pro.67
Lone pair ... pi interactions between water oxygens and aromatic residues: quantum chemical studies based on high-resolution protein structures and model compounds
Abstract
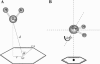
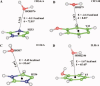
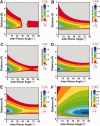
The pi electron cloud of aromatic centers is known to be involved in several noncovalent interactions such as C--H...pi, O--H...pi, and pi...pi interactions in biomolecules. Lone-pair (lp) ... pi interactions have gained attention recently and their role in biomolecular structures is being recognized. In this article, we have carried out systematic analysis of high-resolution protein structures and identified more than 400 examples in which water oxygen atoms are in close contact (distance < 3.5 A) with the aromatic centers of aromatic residues. Three different methods were used to build hydrogen atoms and we used a consensus approach to find out potential candidates for lp...pi interactions between water oxygen and aromatic residues. Quantum mechanical calculations at MP2/6-311++G(d,p) level on model systems based on protein structures indicate that majority of the identified examples have energetically favorable interactions. The influence of water hydrogen atoms was investigated by sampling water orientations as a function of two parameters: distance from the aromatic center and the angle between the aromatic plane and the plane formed by the three water atoms. Intermolecular potential surfaces were constructed using six model compounds representing the four aromatic amino acids and 510 different water orientations for each model compound. Ab initio molecular orbital calculations at MP2/6-311++G(d,p) level show that the interaction energy is favorable even when hydrogen atoms are farthest from the aromatic plane while water oxygen is pointing toward the aromatic center. The strength of such interaction depends upon the distance of water hydrogen atoms from the aromatic substituents. Our calculations clearly show that the lp...pi interactions due to the close approach of water oxygen and aromatic center are influenced by the positions of water hydrogen atoms and the aromatic substituents.
Figures
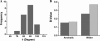

Similar articles
-
Close contacts between carbonyl oxygen atoms and aromatic centers in protein structures: pi...pi or lone-pair...pi interactions?J Phys Chem B. 2007 Aug 2;111(30):8680-3. doi: 10.1021/jp072742l. Epub 2007 Jul 7. J Phys Chem B. 2007. PMID: 17616223
-
Oxygen-aromatic contacts in intra-strand base pairs: analysis of high-resolution DNA crystal structures and quantum chemical calculations.J Struct Biol. 2014 Jul;187(1):49-57. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2014.04.008. Epub 2014 May 9. J Struct Biol. 2014. PMID: 24816369
-
Interaction of aromatic units of amino acids with guanidinium cation: The interplay of π···π, X-H···π, and M+ ···π contacts.J Comput Chem. 2014 Jun 30;35(17):1290-301. doi: 10.1002/jcc.23623. Epub 2014 Apr 25. J Comput Chem. 2014. PMID: 24771291
-
Lone pair-π interactions in biological systems: occurrence, function, and physical origin.Eur Biophys J. 2017 Dec;46(8):729-737. doi: 10.1007/s00249-017-1210-1. Epub 2017 May 2. Eur Biophys J. 2017. PMID: 28466098 Review.
-
Aromatic interactions in model systems.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2002 Dec;6(6):736-41. doi: 10.1016/s1367-5931(02)00359-9. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2002. PMID: 12470725 Review.
Cited by
-
Structural basis of the induced-fit mechanism of 1,4-dihydroxy-2-naphthoyl coenzyme A synthase from the crotonase fold superfamily.PLoS One. 2013 Apr 26;8(4):e63095. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0063095. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23658663 Free PMC article.
-
Unconventional N-H…N Hydrogen Bonds Involving Proline Backbone Nitrogen in Protein Structures.Biophys J. 2016 May 10;110(9):1967-79. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2016.03.034. Biophys J. 2016. PMID: 27166805 Free PMC article.
-
Heptacarbonyl-1κC,2κC-(4-phenyl-pyridine-1κN)di-μ-phenyltellurido-1:2κTe:Te-dirhenium(I).Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2010 Apr 14;66(Pt 5):m518-9. doi: 10.1107/S1600536810012389. Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2010. PMID: 21579015 Free PMC article.
-
High-resolution structure of the amino acid transporter AdiC reveals insights into the role of water molecules and networks in oligomerization and substrate binding.BMC Biol. 2021 Aug 30;19(1):179. doi: 10.1186/s12915-021-01102-4. BMC Biol. 2021. PMID: 34461897 Free PMC article.
-
A computational study on the role of noncovalent interactions in the stability of polymer/graphene nanocomposites.J Mol Model. 2017 Feb;23(2):43. doi: 10.1007/s00894-017-3214-2. Epub 2017 Feb 2. J Mol Model. 2017. PMID: 28154980
References
-
- Li Z, Lazaridis T. Water at biomolecular binding interfaces. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2007;9:573–581. - PubMed
-
- Loris R, Langhorst U, Vos SD, Decanniere K, Bouckaert J, Maes D, Transue TR, Steyaert J. Conserved water molecules in a large family of microbial ribonucleases. Proteins: Struct Funct Genet. 1999;36:117–134. - PubMed
-
- Scheidig AJ, Burmester C, Goody RS. The pre-hydrolysis state of p21ras in complex with GTP: new insights into the role of water molecules in the GTP hydrolysis reaction of ras-like proteins. Structure. 1999;7:1311–1324. - PubMed
-
- Tarek M, Tobias DJ. Environmental dependence of the dynamics of protein hydration water. J Am Chem Soc. 1999;121:9740–9741.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

