Transglutaminase-1 gene mutations in autosomal recessive congenital ichthyosis: summary of mutations (including 23 novel) and modeling of TGase-1
- PMID: 19241467
- PMCID: PMC3243309
- DOI: 10.1002/humu.20952
Transglutaminase-1 gene mutations in autosomal recessive congenital ichthyosis: summary of mutations (including 23 novel) and modeling of TGase-1
Abstract
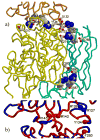
Autosomal recessive congenital ichthyosis (ARCI) is a heterogeneous group of rare cornification diseases. Germline mutations in TGM1 are the most common cause of ARCI in the United States. TGM1 encodes for the TGase-1 enzyme that functions in the formation of the cornified cell envelope. Structurally defective or attenuated cornified cell envelop have been shown in epidermal scales and appendages of ARCI patients with TGM1 mutations. We review the clinical manifestations as well as the molecular genetics of ARCI. In addition, we characterized 115 TGM1 mutations reported in 234 patients from diverse racial and ethnic backgrounds (Caucasion Americans, Norwegians, Swedish, Finnish, German, Swiss, French, Italian, Dutch, Portuguese, Hispanics, Iranian, Tunisian, Moroccan, Egyptian, Afghani, Hungarian, African Americans, Korean, Japanese and South African). We report 23 novel mutations: 71 (62%) missense; 20 (17%) nonsense; 9 (8%) deletion; 8 (7%) splice-site, and 7 (6%) insertion. The c.877-2A>G was the most commonly reported TGM1 mutation accounting for 34% (147 of 435) of all TGM1 mutant alleles reported to date. It had been shown that this mutation is common among North American and Norwegian patients due to a founder effect. Thirty-one percent (36 of 115) of all mutations and 41% (29 of 71) of missense mutations occurred in arginine residues in TGase-1. Forty-nine percent (35 of 71) of missense mutations were within CpG dinucleotides, and 74% (26/35) of these mutations were C>T or G>A transitions. We constructed a model of human TGase-1 and showed that all mutated arginines that reside in the two beta-barrel domains and two (R142 and R143) in the beta-sandwich are located at domain interfaces. In conclusion, this study expands the TGM1 mutation spectrum and summarizes the current knowledge of TGM1 mutations. The high frequency of mutated arginine codons in TGM1 may be due to the deamination of 5' methylated CpG dinucleotides.
(c) 2009 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures

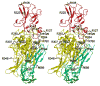
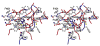
Similar articles
-
Novel transglutaminase-1 mutations and genotype-phenotype investigations of 104 patients with autosomal recessive congenital ichthyosis in the USA.J Med Genet. 2009 Feb;46(2):103-11. doi: 10.1136/jmg.2008.060905. Epub 2008 Oct 23. J Med Genet. 2009. PMID: 18948357 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and functional characterization of a novel transglutaminase 1 gene mutation associated with autosomal recessive congenital ichthyosis.Int J Dermatol. 2016 Feb;55(2):201-7. doi: 10.1111/ijd.12806. Epub 2015 Jul 28. Int J Dermatol. 2016. PMID: 26220141
-
A novel TGM1 mutation, leading to multiple splicing rearrangements, is associated with autosomal recessive congenital ichthyosis.Clin Exp Dermatol. 2015 Oct;40(7):757-60. doi: 10.1111/ced.12627. Epub 2015 Mar 9. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2015. PMID: 25754682
-
Mutations of transglutaminase-1 in Chinese patients with autosomal recessive congenital ichthyosis: a case report with clinical and genetic analysis of Chinese cases reported in literature.Clin Exp Dermatol. 2015 Jan;40(1):56-62. doi: 10.1111/ced.12410. Epub 2014 Aug 22. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2015. PMID: 25154629 Review.
-
Update on autosomal recessive congenital ichthyosis: mRNA analysis using hair samples is a powerful tool for genetic diagnosis.J Dermatol Sci. 2015 Jul;79(1):4-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2015.04.009. Epub 2015 Apr 30. J Dermatol Sci. 2015. PMID: 25982146 Review.
Cited by
-
Correction of the pathogenic mutation in TGM1 gene by adenine base editing in mutant embryos.Mol Ther. 2022 Jan 5;30(1):175-183. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2021.05.007. Epub 2021 May 8. Mol Ther. 2022. PMID: 33974999 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic approaches for celiac disease.Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2015 Jun;29(3):503-21. doi: 10.1016/j.bpg.2015.04.005. Epub 2015 May 9. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26060114 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of lipoxygenases in pathophysiology; new insights and future perspectives.Redox Biol. 2015 Dec;6:297-310. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2015.08.006. Epub 2015 Aug 7. Redox Biol. 2015. PMID: 26298204 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transglutaminase1 preferred substrate peptide K5 is an efficient tool in diagnosis of lamellar ichthyosis.Am J Pathol. 2010 Apr;176(4):1592-9. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2010.090597. Epub 2010 Feb 18. Am J Pathol. 2010. PMID: 20167857 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid Nanoparticle-Mediated Hit-and-Run Approaches Yield Efficient and Safe In Situ Gene Editing in Human Skin.ACS Nano. 2023 Nov 14;17(21):22046-22059. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.3c08644. Epub 2023 Nov 2. ACS Nano. 2023. PMID: 37918441 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akiyama M, Takizawa Y, Kokaji T, Shimizu H. Novel mutations of TGM1 in a child with congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma. Br J Dermatol. 2001a;144:401–407. - PubMed
-
- Akiyama M, Takizawa Y, Suzuki Y, Ishiko A, Matsuo I, Shimizu H. Compound heterozygous TGM1 mutations including a novel missense mutation L204Q in a mild form of lamellar ichthyosis. J Invest Dermatol. 2001b;116:992–995. - PubMed
-
- Akiyama M, Takizawa Y, Suzuki Y, Shimizu H. A novel homozygous mutation 371delA in TGM1 leads to a classic lamellar ictiosis phenotype. Br J Dermatol. 2003;148:149–153. - PubMed
-
- Akiyama M, Sugiyama-Nakagiri Y, Sakai K, McMillan JR, Goto M, Arita K, Tsuji-Abe Y, Tabata N, Matsuoka K, Sasaki R, Sawamura D, Shimizu H. Mutations in lipid transporter ABCA12 in harlequin ichthyosis and functional recovery by corrective gene transfer. J Clin Invest. 2005;115:1777–1784. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

