Combination of cladribine and cytarabine is effective for childhood acute myeloid leukemia: results of the St Jude AML97 trial
- PMID: 19242495
- PMCID: PMC2726271
- DOI: 10.1038/leu.2009.30
Combination of cladribine and cytarabine is effective for childhood acute myeloid leukemia: results of the St Jude AML97 trial
Abstract
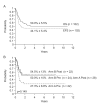
Because cladribine can increase cytarabine triphosphate levels, we tested a cladribine-cytarabine combination in the St Jude AML97, trial in which this combination was administered before standard chemotherapy to 96 children with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) or myelodysplastic syndrome. Patients received a 5-day course of cladribine (9 mg/m(2) per dose) and cytarabine either as daily 2-h infusions (500 mg/m(2) per dose) (arm A) or a continuous infusion (500 mg/m(2) per day) (arm B). Ara-CTP levels and inhibition of DNA synthesis increased from day 1 to day 2, but were not different between the two arms. In addition, the median blast percentages at day 15 did not differ between arms A and B, but patients treated in arm A had shorter intervals between the initiation of the first and second courses of therapy. Thus, although there were trends toward better complete remission rates and overall survival for patients treated in arm B, the reduced efficacy of arm A may have been partially compensated by more intense timing of therapy for that group. For all patients, 5-year event-free survival and overall survival estimates were 44.1+/-5.4 and 50.0+/-5.5%. Our results suggest that cladribine in combination with continuous-infusion cytarabine is effective therapy for childhood AML.
Figures

References
-
- Creutzig U, Zimmermann M, Lehrnbecher T, Graf N, Hermann J, Niemeyer CM, et al. Less toxicity by optimizing chemotherapy, but not by addition of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in children and adolescents with acute myeloid leukemia: results of AML-BFM 98. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:4499–4506. - PubMed
-
- Kaspers GJ, Creutzig U. Pediatric acute myeloid leukemia: international progress and future directions. Leukemia. 2005;19:2025–2029. - PubMed
-
- Robertson LE, Chubb S, Meyn RE, Story M, Ford R, Hittelman WN, et al. Induction of apoptotic cell death in chronic lymphocytic leukemia by 2- chloro-2′-deoxyadenosine and 9-beta-D-arabinosyl-2-fluoroadenine. Blood. 1993;81:143–150. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

