Depletion of kinesin 5B affects lysosomal distribution and stability and induces peri-nuclear accumulation of autophagosomes in cancer cells
- PMID: 19242560
- PMCID: PMC2647799
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0004424
Depletion of kinesin 5B affects lysosomal distribution and stability and induces peri-nuclear accumulation of autophagosomes in cancer cells
Abstract
Background: Enhanced lysosomal trafficking is associated with metastatic cancer. In an attempt to discover cancer relevant lysosomal motor proteins, we compared the lysosomal proteomes from parental MCF-7 breast cancer cells with those from highly invasive MCF-7 cells that express an active form of the ErbB2 (DeltaN-ErbB2).
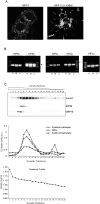
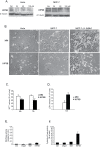
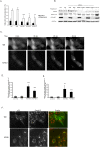
Methodology/principal findings: Mass spectrometry analysis identified kinesin heavy chain protein KIF5B as the only microtubule motor associated with the lysosomes in MCF-7 cells, and ectopic DeltaN-ErbB2 enhanced its lysosomal association. KIF5B associated with lysosomes also in HeLa cervix carcinoma cells as analyzed by subcellular fractionation. The depletion of KIF5B triggered peripheral aggregations of lysosomes followed by lysosomal destabilization, and cell death in HeLa cells. Lysosomal exocytosis in response to plasma membrane damage as well as fluid phase endocytosis functioned, however, normally in these cells. Both HeLa and MCF-7 cells appeared to express similar levels of the KIF5B isoform but the death phenotype was weaker in KIF5B-depleted MCF-7 cells. Surprisingly, KIF5B depletion inhibited the rapamycin-induced accumulation of autophagosomes in MCF-7 cells. In KIF5B-depleted cells the autophagosomes formed and accumulated in the close proximity to the Golgi apparatus, whereas in the control cells they appeared uniformly distributed in the cytoplasm.
Conclusions/significance: Our data identify KIF5B as a cancer relevant lysosomal motor protein with additional functions in autophagosome formation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Eskelinen EL, Tanaka Y, Saftig P. At the acidic edge: emerging functions for lysosomal membrane proteins. Trends Cell Biol. 2003;13:137–145. - PubMed
-
- Gieselmann V. Lysosomal storage diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1995;1270:103–136. - PubMed
-
- Gocheva V, Joyce JA. Cysteine cathepsins and the cutting edge of cancer invasion. Cell Cycle. 2007;6:60–64. - PubMed
-
- Jedeszko C, Sloane BF. Cysteine cathepsins in human cancer. Biol Chem. 2004;385:1017–1027. - PubMed
-
- Fehrenbacher N, Gyrd-Hansen M, Poulsen B, Felbor U, Kallunki T, et al. Sensitization to the lysosomal cell death pathway upon immortalization and transformation. Cancer Res. 2004;64:5301–5310. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

