Cardioprotection and altered mitochondrial adenine nucleotide transport
- PMID: 19242642
- PMCID: PMC3399173
- DOI: 10.1007/s00395-009-0002-x
Cardioprotection and altered mitochondrial adenine nucleotide transport
Abstract
It is becoming increasingly clear that mitochondrial dysfunction is critically important in myocardial ischemic injury, and that cardioprotective mechanisms must ultimately prevent or attenuate mitochondrial damage. Mitochondria are also essential for energy production, and therefore prevention of mitochondrial injury must not compromise oxidative phosphorylation during reperfusion. This review will focus on one mitochondrial mechanism of cardioprotection involving inhibition of adenine nucleotide transport across the outer mitochondria membrane under de-energized conditions. This slows ATP hydrolysis by the mitochondria, and would be expected to lower mitochondrial membrane potential during ischemia, to inhibit calcium uptake during ischemia, and potentially to reduce free radical generation during early reperfusion. Two interventions that similarly inhibit mitochondrial adenine nucleotide transport are Bcl-2 overexpression and GSK inhibition. A possible final common mechanism shared by both of these interventions is discussed.
Figures


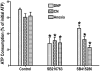



References
-
- Murry CE, Jennings RB, Reimer KA. Preconditioning with ischemia: a delay of lethal cell injury in ischemic myocardium. Circulation. 1986;74(5):1124–1136. - PubMed
-
- Murry CE, Richard VJ, Reimer KA, Jennings RB. Ischemic preconditioning slows energy metabolism and delays ultrastructural damage during a sustained ischemic episode. Circ Res. 1990;66(4):913–931. - PubMed
-
- Steenbergen C, Perlman ME, London RE, Murphy E. Mechanism of preconditioning. Ionic alterations. Circ Res. 1993;72(1):112–125. - PubMed
-
- Asimakis GK, Inners-McBride K, Medellin G, Conti VR. Ischemic preconditioning attenuates acidosis and postischemic dysfunction in isolated rat heart. Am J Physiol. 1992;263(3 Pt 2):H887–894. - PubMed
-
- Imahashi K, Schneider MD, Steenbergen C, Murphy E. Transgenic expression of Bcl-2 modulates energy metabolism, prevents cytosolic acidification during ischemia, and reduces ischemia/reperfusion injury. Circ Res. 2004;95(7):734–741. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

