Metabolic stress-like condition can be induced by prolonged strenuous exercise in athletes
- PMID: 19242868
- PMCID: PMC2852746
- DOI: 10.1080/03009730802579778
Metabolic stress-like condition can be induced by prolonged strenuous exercise in athletes
Abstract
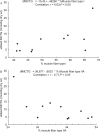
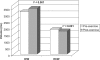
Few studies have examined energy metabolism during prolonged, strenuous exercise. We wanted therefore to investigate energy metabolic consequences of a prolonged period of continuous strenuous work with very high energy expenditure. Twelve endurance-trained athletes (6 males and 6 females) were recruited. They performed a 7-h bike race on high work-load intensity. Physiological, biochemical, endocrinological, and anthropometric muscular compartment variables were monitored before, during, and after the race. The energy expenditure was high, being 5557 kcal. Work-load intensity (% of VO(2) peak) was higher in females (77.7%) than in men (69.9%). Muscular glycogen utilization was pronounced, especially in type I fibres (>90%). Additionally, muscular triglyceride lipolysis was considerably accelerated. Plasma glucose levels were increased concomitantly with an unchanged serum insulin concentration which might reflect an insulin resistance state in addition to proteolytic glyconeogenesis. Increased reactive oxygen species (malondialdehyde (MDA)) were additional signs of metabolic stress. MDA levels correlated with glycogen utilization rate. A relative deficiency of energy substrate on a cellular level was indicated by increased intracellular water of the leg muscle concomitantly with increased extracellular levels of the osmoregulatory amino acid taurine. A kindred nature of a presumed insulin-resistant state with less intracellular availability of glucose for erythrocytes was also indicated by the findings of decreased MCV together with increased MCHC (haemoconcentration) after the race. This strenuous energy-demanding work created a metabolic stress-like condition including signs of insulin resistance and deteriorated intracellular glucose availability leading to compromised fuelling of ion pumps, culminating in a disturbed cellular osmoregulation indicated by taurine efflux and cellular swelling.
Figures
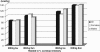


Similar articles
-
Muscle triglyceride and glycogen in endurance exercise: implications for performance.Sports Med. 2004;34(3):151-64. doi: 10.2165/00007256-200434030-00002. Sports Med. 2004. PMID: 14987125 Review.
-
The regulation of carbohydrate and fat metabolism during and after exercise.Front Biosci. 1998 Sep 15;3:D1011-27. doi: 10.2741/a342. Front Biosci. 1998. PMID: 9740552 Review.
-
Intramyocellular lipids form an important substrate source during moderate intensity exercise in endurance-trained males in a fasted state.J Physiol. 2003 Dec 1;553(Pt 2):611-25. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.052431. Epub 2003 Sep 26. J Physiol. 2003. PMID: 14514877 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Gender differences in substrate utilization during submaximal exercise in endurance-trained subjects.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2002 Feb;282(2):E435-47. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00266.2001. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2002. PMID: 11788377
-
Low-fat diet alters intramuscular substrates and reduces lipolysis and fat oxidation during exercise.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2001 Mar;280(3):E391-8. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.2001.280.3.E391. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2001. PMID: 11171592 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Circulating cell-free DNA: an up-coming molecular marker in exercise physiology.Sports Med. 2012 Jul 1;42(7):565-86. doi: 10.2165/11631380-000000000-00000. Sports Med. 2012. PMID: 22694348 Review.
-
Multi-frequency bioimpedance in human muscle assessment.Physiol Rep. 2015 Apr;3(4):e12354. doi: 10.14814/phy2.12354. Physiol Rep. 2015. PMID: 25896978 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hartley LH, Mason JW, Hogan RP, Jones LG, Kotchen TA, Mougey EH, et al. Multiple hormonal responses to prolonged exercise in relation to physical training. J Appl Physiol. 1972;33:607–10. - PubMed
-
- Coyle EF. Physical activity as a metabolic stressor. Am J Clin Nutr. 2000;72:512S–20S. - PubMed
-
- Cuisinier C, Ward RJ, Francaux M, Sturbois X, de Witte P. Changes in plasma and urinary taurine and amino acids in runners immediately and 24h after marathon. Amino Acids. 2001;20:13–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
