Two distinct signalling cascades target the NF-kappaB regulatory factor c-IAP1 for degradation
- PMID: 19243308
- PMCID: PMC2677214
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20082140
Two distinct signalling cascades target the NF-kappaB regulatory factor c-IAP1 for degradation
Abstract
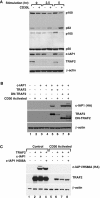
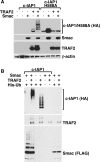
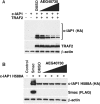
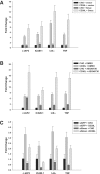
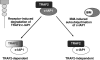
c-IAP1 (cellular inhibitor of apoptosis 1) has recently emerged as a negative regulator of the non-canonical NF-kappaB (nuclear factor kappaB) signalling cascade. Whereas synthetic IAP inhibitors have been shown to trigger the autoubiquitination and degradation of c-IAP1, less is known about the physiological mechanisms by which c-IAP1 stability is regulated. In the present paper, we describe two distinct cellular processes that lead to the targeted loss of c-IAP1. Recruitment of a TRAF2 (tumour necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 2)-c-IAP1 complex to the cytoplasmic domain of the Hodgkin's/anaplastic large-cell lymphoma-associated receptor, CD30, leads to the targeting and degradation of the TRAF2-c-IAP1 heterodimer through a mechanism requiring the RING (really interesting new gene) domain of TRAF2, but not c-IAP1. In contrast, the induced autoubiquitination of c-IAP1 by IAP antagonists causes the selective loss of c-IAP1, but not TRAF2, thereby releasing TRAF2. Thus c-IAP1 can be targeted for degradation by two distinct processes, revealing the critical importance of this molecule as a regulator of numerous intracellular signalling cascades.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Ubiquitin binding modulates IAP antagonist-stimulated proteasomal degradation of c-IAP1 and c-IAP2(1).Biochem J. 2009 Jan 1;417(1):149-60. doi: 10.1042/BJ20081885. Biochem J. 2009. PMID: 18939944
-
Enhanced cytoprotective effects of the inhibitor of apoptosis protein cellular IAP1 through stabilization with TRAF2.J Biol Chem. 2009 Jul 31;284(31):20531-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.029983. Epub 2009 Jun 8. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19506082 Free PMC article.
-
TNF-RII and c-IAP1 mediate ubiquitination and degradation of TRAF2.Nature. 2002 Mar 21;416(6878):345-7. doi: 10.1038/416345a. Nature. 2002. PMID: 11907583
-
TRAF2 multitasking in TNF receptor-induced signaling to NF-κB, MAP kinases and cell death.Biochem Pharmacol. 2016 Sep 15;116:1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2016.03.009. Epub 2016 Mar 16. Biochem Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26993379 Review.
-
Targeting signaling factors for degradation, an emerging mechanism for TRAF functions.Immunol Rev. 2015 Jul;266(1):56-71. doi: 10.1111/imr.12311. Immunol Rev. 2015. PMID: 26085207 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
IAP inhibitors enhance co-stimulation to promote tumor immunity.J Exp Med. 2010 Sep 27;207(10):2195-206. doi: 10.1084/jem.20101123. Epub 2010 Sep 13. J Exp Med. 2010. PMID: 20837698 Free PMC article.
-
Degradation of cIAPs contributes to hepatocyte lipoapoptosis.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2013 Nov;305(9):G611-9. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00111.2013. Epub 2013 Sep 5. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2013. PMID: 24008361 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitor of apoptosis proteins as intracellular signaling intermediates.FEBS J. 2016 Jan;283(2):221-31. doi: 10.1111/febs.13554. Epub 2015 Nov 4. FEBS J. 2016. PMID: 26462035 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular inhibitor of apoptosis 1 (cIAP-1) degradation by caspase 8 during TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-induced apoptosis.Exp Cell Res. 2011 Jan 1;317(1):107-16. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2010.10.005. Epub 2010 Oct 14. Exp Cell Res. 2011. PMID: 20951133 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of physiological and synthetic IAP antagonism on c-IAP-dependent signaling.Oncogene. 2015 Oct;34(43):5472-81. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.3. Epub 2015 Feb 9. Oncogene. 2015. PMID: 25659587 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stein H., Foss H. D., Dürkop H., Marafioti T., Delsol G., Pulford K., Pileri S., Falini B. CD30+ anaplastic large cell lymphoma: a review of its histopathologic, genetic, and clinical features. Blood. 2000;96:3681–3695. - PubMed
-
- Younes A., Carbone A. CD30/CD30 ligand and CD40/CD40 ligand in malignant lymphoid disorders. Int. J. Biol. Markers. 1999;14:135–143. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

