Knockdown of c-FLIP(L) enhanced AD5-10 anti-death receptor 5 monoclonal antibody-induced apoptosis in human lung cancer cells
- PMID: 19243385
- PMCID: PMC11158711
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2009.01119.x
Knockdown of c-FLIP(L) enhanced AD5-10 anti-death receptor 5 monoclonal antibody-induced apoptosis in human lung cancer cells
Erratum in
- Cancer Sci. 2009 Dec;100(12):2469
Abstract
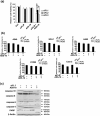
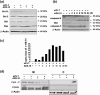
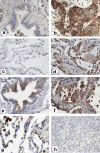
It is reported that the agonistic antibodies against death receptors 4 and 5 (DR4, DR5) are cytotoxic to various cancer cells. In the present study, the sensitivity of five human lung cancer cell lines to previously reported AD5-10 agonistic antibody against DR5 were investigated. Of these cell lines, A549 and small cell lung cancer showed a moderate sensitivity to AD5-10 and three other cell lines were resistant. Cell line H460 is resistant to AD5-10 despite a high level of cell-surface DR5 expression. We demonstrated that the resistance of H460 cells to AD5-10 was not related to the expression level of DR5, but the expression and cleavage of c-FLIP(L) in the cells. Inhibition of endogenous c-FLIP(L) expression by siRNA significantly enhanced AD5-10-induced cell death in these lung cancer cells. We further showed that this sensitizing effect was associated with decreased expression of Bcl-2 family proteins Bid and Bcl-X(L), change of mitochondrial membrane potential, release of cytochrome c from mitochondria, and caspase activation. Therefore, these data provide evidence that c-FLIP(L) is involved in the resistance of lung cancer cells to AD5-10-induced apoptosis. Moreover, immunohistochemistry on paraffin-embedded tissue revealed that c-FLIP(L) was expressed in 87.9% (29 of 33) of lung carcinoma tissues from the patients, but little in tissues from normal controls. This suggests that inhibition of c-FLIP(L) expression might be a potential strategy for lung cancer therapy, especially for those lung cancers resistant to the agonistic antibody against death receptors.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Suppression of HSP70 expression sensitizes NSCLC cell lines to TRAIL-induced apoptosis by upregulating DR4 and DR5 and downregulating c-FLIP-L expressions.J Mol Med (Berl). 2013 Feb;91(2):219-35. doi: 10.1007/s00109-012-0947-3. Epub 2012 Sep 5. J Mol Med (Berl). 2013. PMID: 22948392
-
The eIF4E/eIF4G interaction inhibitor 4EGI-1 augments TRAIL-mediated apoptosis through c-FLIP Down-regulation and DR5 induction independent of inhibition of cap-dependent protein translation.Neoplasia. 2010 Apr;12(4):346-56. doi: 10.1593/neo.10144. Neoplasia. 2010. PMID: 20360945 Free PMC article.
-
PPARgamma ligands enhance TRAIL-induced apoptosis through DR5 upregulation and c-FLIP downregulation in human lung cancer cells.Cancer Biol Ther. 2007 Jan;6(1):99-106. doi: 10.4161/cbt.6.1.3555. Cancer Biol Ther. 2007. PMID: 17172826
-
Down-regulation of intracellular anti-apoptotic proteins, particularly c-FLIP by therapeutic agents; the novel view to overcome resistance to TRAIL.J Cell Physiol. 2018 Oct;233(10):6470-6485. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26585. Epub 2018 May 9. J Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29741767 Review.
-
c-FLIP, a master anti-apoptotic regulator.Exp Oncol. 2012 Oct;34(3):176-84. Exp Oncol. 2012. PMID: 23070002 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
4-(4-Chloro-2-methylphenoxy)-N-hydroxybutanamide (CMH) targets mRNA of the c-FLIP variants and induces apoptosis in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells.Mol Cell Biochem. 2010 Sep;342(1-2):133-142. doi: 10.1007/s11010-010-0477-7. Epub 2010 May 6. Mol Cell Biochem. 2010. PMID: 20446019 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting a novel N-terminal epitope of death receptor 5 triggers tumor cell death.J Biol Chem. 2010 Mar 19;285(12):8953-66. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.070680. Epub 2010 Jan 27. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20106985 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of PI3Kcb utilizing adenovirus-mediated transfer of siRNA attenuates bone cancer pain.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014 Oct 15;7(11):8127-35. eCollection 2014. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014. PMID: 25550861 Free PMC article.
-
PARP-1 regulates resistance of pancreatic cancer to TRAIL therapy.Clin Cancer Res. 2013 Sep 1;19(17):4750-9. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-0516. Epub 2013 Jul 5. Clin Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23833311 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Greenlee RT, Hill‐Harmon MB, Murray T, Thun M. Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 2001; 51: 15–36. - PubMed
-
- Ferreira CG, Huisman C, Giaccone G. Novel approaches to the treatment of non‐small cell lung cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 2002; 41: 57–77. - PubMed
-
- Carlo‐Stella C, Lavazza C, Locatelli A, Vigano L, Gianni AM, Gianni L. Targeting TRAIL agonistic receptors for cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res 2007; 13: 2313–7. - PubMed
-
- Walczak H, Miller RE, Ariail K et al . Tumoricidal activity of tumor necrosis factor‐related apoptos‐inducing ligand in vivo . Nat Med 1999; 5: 157–63. - PubMed
-
- Zhang L, Zhang X, Barrisford GW, Olumi AF. Lexatumumab (TRAIL‐receptor 2 mAb) induces expression of DR5 and promotes apoptosis in primary and metastatic renal cell carcinoma in a mouse orthotopic model. Cancer Lett 2007; 251: 146–57. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

