Zinc transporter gene expression is regulated by pro-inflammatory cytokines: a potential role for zinc transporters in beta-cell apoptosis?
- PMID: 19243577
- PMCID: PMC2651882
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6823-9-7
Zinc transporter gene expression is regulated by pro-inflammatory cytokines: a potential role for zinc transporters in beta-cell apoptosis?
Abstract
Background: Beta-cells are extremely rich in zinc and zinc homeostasis is regulated by zinc transporter proteins. beta-cells are sensitive to cytokines, interleukin-1beta (IL-1beta) has been associated with beta-cell dysfunction and -death in both type 1 and type 2 diabetes. This study explores the regulation of zinc transporters following cytokine exposure.
Methods: The effects of cytokines IL-1beta, interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma), and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) on zinc transporter gene expression were measured in INS-1-cells and rat pancreatic islets. Being the more sensitive transporter, we further explored ZnT8 (Slc30A8): the effect of ZnT8 over expression on cytokine induced apoptosis was investigated as well as expression of the insulin gene and two apoptosis associated genes, BAX and BCL2.
Results: Our results showed a dynamic response of genes responsible for beta-cell zinc homeostasis to cytokines: IL-1beta down regulated a number of zinc-transporters, most strikingly ZnT8 in both islets and INS-1 cells. The effect was even more pronounced when mixing the cytokines. TNF-alpha had little effect on zinc transporter expression. IFN-gamma down regulated a number of zinc transporters. Insulin expression was down regulated by all cytokines. ZnT8 over expressing cells were more sensitive to IL-1beta induced apoptosis whereas no differences were observed with IFN-gamma, TNF-alpha, or a mixture of cytokines.
Conclusion: The zinc transporting system in beta-cells is influenced by the exposure to cytokines. Particularly ZnT8, which has been associated with the development of diabetes, seems to be cytokine sensitive.
Figures

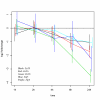
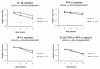
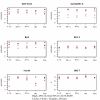
Similar articles
-
Lack of ZnT8 protects pancreatic islets from hypoxia- and cytokine-induced cell death.J Endocrinol. 2022 Feb 11;253(1):1-11. doi: 10.1530/JOE-21-0271. J Endocrinol. 2022. PMID: 35017316 Free PMC article.
-
Down-regulation of the islet-specific zinc transporter-8 (ZnT8) protects human insulinoma cells against inflammatory stress.J Biol Chem. 2019 Nov 8;294(45):16992-17006. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.010937. Epub 2019 Oct 7. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 31591269 Free PMC article.
-
STAT5 activation by human GH protects insulin-producing cells against interleukin-1beta, interferon-gamma and tumour necrosis factor-alpha-induced apoptosis independent of nitric oxide production.J Endocrinol. 2005 Oct;187(1):25-36. doi: 10.1677/joe.1.06086. J Endocrinol. 2005. PMID: 16214938
-
Role of pro-inflammatory cytokines of pancreatic islets and prospects of elaboration of new methods for the diabetes treatment.Acta Biochim Pol. 2015;62(1):15-21. doi: 10.18388/abp.2014_853. Epub 2015 Mar 18. Acta Biochim Pol. 2015. PMID: 25781159 Review.
-
Zinc transporters and their role in the pancreatic β-cell.J Diabetes Investig. 2012 Jun 6;3(3):202-11. doi: 10.1111/j.2040-1124.2012.00199.x. J Diabetes Investig. 2012. PMID: 24843567 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Differential DNA methylation and expression of inflammatory and zinc transporter genes defines subgroups of osteoarthritic hip patients.Ann Rheum Dis. 2015 Sep;74(9):1778-82. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-206752. Epub 2015 Apr 8. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015. PMID: 25854584 Free PMC article.
-
ZnT8 Exerts Anti-apoptosis of Kidney Tubular Epithelial Cell in Diabetic Kidney Disease Through TNFAIP3-NF-κB Signal Pathways.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2023 May;201(5):2442-2457. doi: 10.1007/s12011-022-03361-w. Epub 2022 Jul 23. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2023. PMID: 35871203
-
Genetic, Functional, and Immunological Study of ZnT8 in Diabetes.Int J Endocrinol. 2019 Feb 26;2019:1524905. doi: 10.1155/2019/1524905. eCollection 2019. Int J Endocrinol. 2019. PMID: 30936916 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metal Dyshomeostasis as a Driver of Gut Pathology in Autism Spectrum Disorders.J Neurochem. 2025 Mar;169(3):e70041. doi: 10.1111/jnc.70041. J Neurochem. 2025. PMID: 40108935 Free PMC article.
-
TNF-α gene expression is increased following zinc supplementation in type 2 diabetes mellitus.Genes Nutr. 2015 Jan;10(1):440. doi: 10.1007/s12263-014-0440-4. Epub 2014 Nov 15. Genes Nutr. 2015. PMID: 25403095 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

