Genome-scale identification of Caenorhabditis elegans regulatory elements by tiling-array mapping of DNase I hypersensitive sites
- PMID: 19243610
- PMCID: PMC2651899
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-92
Genome-scale identification of Caenorhabditis elegans regulatory elements by tiling-array mapping of DNase I hypersensitive sites
Abstract
Background: A major goal of post-genomics research is the integrated analysis of genes, regulatory elements and the chromatin architecture on a genome-wide scale. Mapping DNase I hypersensitive sites within the nuclear chromatin is a powerful and well-established method of identifying regulatory element candidates.
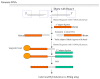
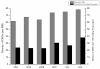
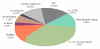
Results: Here, we report the first genome-wide analysis of DNase I hypersensitive sites (DHSs) in Caenorhabditis elegans. The data was obtained by hybridizing DNase I-treated and end-captured material from young adult worms to a high-resolution tiling microarray. The data show that C. elegans DHSs were significantly enriched within intergenic regions located 2 kb upstream and downstream of coding genes, and also that a considerable fraction of all DHSs mapped to intergenic positions distant to annotated coding genes. Annotated transcribed loci were generally depleted in DHSs relative to intergenic regions, but DHSs were nonetheless enriched in coding exons and UTRs, whereas introns were significantly depleted in DHSs. Many DHSs appeared to be associated with annotated non-coding RNAs and recently detected transcripts of unknown function. It has been reported that nematode highly conserved non-coding elements were associated with cis-regulatory elements, and we also found that DHSs, particularly distal intergenic DHSs, were significantly enriched in regions that were conserved between the C. elegans and C. briggsae genomes.
Conclusion: We describe the first genome-wide analysis of C. elegans DHSs, and show that the distribution of DHSs is strongly associated with functional elements in the genome.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genome-wide discovery of active regulatory elements and transcription factor footprints in Caenorhabditis elegans using DNase-seq.Genome Res. 2017 Dec;27(12):2108-2119. doi: 10.1101/gr.223735.117. Epub 2017 Oct 26. Genome Res. 2017. PMID: 29074739 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide mapping of DNase I hypersensitive sites revealed differential chromatin accessibility and regulatory DNA elements under drought stress in rice cultivars.Plant J. 2024 Aug;119(4):2063-2079. doi: 10.1111/tpj.16864. Epub 2024 Jun 10. Plant J. 2024. PMID: 38859561
-
Advances of DNase-seq for mapping active gene regulatory elements across the genome in animals.Gene. 2018 Aug 15;667:83-94. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2018.05.033. Epub 2018 May 14. Gene. 2018. PMID: 29772251 Review.
-
Correlation between DNase I hypersensitive site distribution and gene expression in HeLa S3 cells.PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e42414. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0042414. Epub 2012 Aug 10. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22900019 Free PMC article.
-
Open chromatin in plant genomes.Cytogenet Genome Res. 2014;143(1-3):18-27. doi: 10.1159/000362827. Epub 2014 Jun 6. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2014. PMID: 24923879 Review.
Cited by
-
Chromatin accessibility dynamics reveal novel functional enhancers in C. elegans.Genome Res. 2017 Dec;27(12):2096-2107. doi: 10.1101/gr.226233.117. Epub 2017 Nov 15. Genome Res. 2017. PMID: 29141961 Free PMC article.
-
Distributed probing of chromatin structure in vivo reveals pervasive chromatin accessibility for expressed and non-expressed genes during tissue differentiation in C. elegans.BMC Genomics. 2010 Aug 6;11:465. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-465. BMC Genomics. 2010. PMID: 20691096 Free PMC article.
-
The Caenorhabditis elegans intermediate-size transcriptome shows high degree of stage-specific expression.Nucleic Acids Res. 2011 Jul;39(12):5203-14. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr102. Epub 2011 Mar 4. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011. PMID: 21378118 Free PMC article.
-
Cohesin organizes 3D DNA contacts surrounding active enhancers in C. elegans.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 25:2023.09.18.558239. doi: 10.1101/2023.09.18.558239. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Genome Res. 2025 May 2;35(5):1108-1123. doi: 10.1101/gr.279365.124. PMID: 37786717 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Genome-wide mapping of DNase I hypersensitive sites and association analysis with gene expression in MSB1 cells.Front Genet. 2014 Oct 13;5:308. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2014.00308. eCollection 2014. Front Genet. 2014. PMID: 25352859 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Crawford GE, Holt IE, Whittle J, Webb BD, Tai D, Davis S, Margulies EH, Chen Y, Bernat JA, Ginsburg D, Zhou D, Luo S, Vasicek TJ, Daly MJ, Wolfsberg TG, Collins FS. Genome-wide mapping of DNase hypersensitive sites using massively parallel signature sequencing (MPSS) Genome Res. 2006;16:123–131. doi: 10.1101/gr.4074106. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sabo PJ, Kuehn MS, Thurman R, Johnson BE, Johnson EM, Cao H, Yu M, Rosenzweig E, Goldy J, Haydock A, Weaver M, Shafer A, Lee K, Neri F, Humbert R, Singer MA, Richmond TA, Dorschner MO, McArthur M, Hawrylycz M, Green RD, Navas PA, Noble WS, Stamatoyannopoulos JA. Genome-scale mapping of DNase I sensitivity in vivo using tiling DNA microarrays. Nat Methods. 2006;3:511–518. doi: 10.1038/nmeth890. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

