Epigenetic regulation, somatic homologous recombination, and abscisic acid signaling are influenced by DNA polymerase epsilon mutation in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 19244142
- PMCID: PMC2660612
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.108.061549
Epigenetic regulation, somatic homologous recombination, and abscisic acid signaling are influenced by DNA polymerase epsilon mutation in Arabidopsis
Abstract
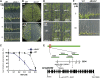
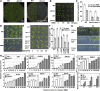
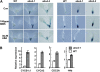
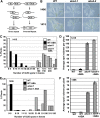
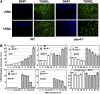
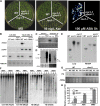
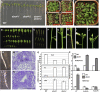
Based on abscisic acid (ABA) inhibition of seed germination and seedling growth assays, we isolated an ABA overly sensitive mutant (abo4-1) caused by a mutation in the Arabidopsis thaliana POL2a/TILTED1(TIL1) gene encoding a catalytic subunit of DNA polymerase epsilon. The dominant, ABA-insensitive abi1-1 or abi2-1 mutations suppressed the ABA hypersensitivity of the abo4-1 mutant. The abo4/til1 mutation reactivated the expression of the silenced Athila retrotransposon transcriptional silent information (TSI) and the silenced 35S-NPTII in the ros1 mutant and increased the frequency of somatic homologous recombination (HR) approximately 60-fold. ABA upregulated the expression of TSI and increased HR in both the wild type and abo4-1. MEIOTIC RECOMBINATION11 and GAMMA RESPONSE1, both of which are required for HR and double-strand DNA break repair, are expressed at higher levels in abo4-1 and are enhanced by ABA, while KU70 was suppressed by ABA. abo4-1 mutant plants are sensitive to UV-B and methyl methanesulfonate and show constitutive expression of the G2/M-specific cyclin CycB1;1 in meristems. The abo4-1 plants were early flowering with lower expression of FLOWER LOCUS C and higher expression of FLOWER LOCUS T and changed histone modifications in the two loci. Our results suggest that ABO4/POL2a/TIL1 is involved in maintaining epigenetic states, HR, and ABA signaling in Arabidopsis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Abscisic acid suppresses the highly occurred somatic homologous recombination in Arabidopsis rfc1 mutant.J Genet Genomics. 2013 Sep 20;40(9):465-71. doi: 10.1016/j.jgg.2013.05.006. Epub 2013 Jun 10. J Genet Genomics. 2013. PMID: 24053948
-
Homologous Recombination Defective Arabidopsis Mutants Exhibit Enhanced Sensitivity to Abscisic Acid.PLoS One. 2017 Jan 3;12(1):e0169294. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0169294. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28046013 Free PMC article.
-
Mutation in the catalytic subunit of DNA polymerase alpha influences transcriptional gene silencing and homologous recombination in Arabidopsis.Plant J. 2010 Jan;61(1):36-45. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2009.04026.x. Epub 2009 Sep 21. Plant J. 2010. PMID: 19769574
-
Trithorax-group proteins ARABIDOPSIS TRITHORAX4 (ATX4) and ATX5 function in abscisic acid and dehydration stress responses.New Phytol. 2018 Mar;217(4):1582-1597. doi: 10.1111/nph.14933. Epub 2017 Dec 18. New Phytol. 2018. PMID: 29250818
-
Plant hormone signaling and modulation of DNA repair under stressful conditions.Plant Cell Rep. 2013 Jul;32(7):1043-52. doi: 10.1007/s00299-013-1410-9. Epub 2013 Mar 19. Plant Cell Rep. 2013. PMID: 23508254 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanisms for Abscisic Acid Inhibition of Primary Root Growth.Plant Signal Behav. 2018;13(9):e1500069. doi: 10.1080/15592324.2018.1500069. Epub 2018 Aug 6. Plant Signal Behav. 2018. PMID: 30081737 Free PMC article.
-
Auxin Response Factor2 (ARF2) and its regulated homeodomain gene HB33 mediate abscisic acid response in Arabidopsis.PLoS Genet. 2011 Jul;7(7):e1002172. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002172. Epub 2011 Jul 14. PLoS Genet. 2011. PMID: 21779177 Free PMC article.
-
The role of ATXR6 expression in modulating genome stability and transposable element repression in Arabidopsis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Jan 18;119(3):e2115570119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2115570119. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 35027454 Free PMC article.
-
An insight into understanding the coupling between homologous recombination mediated DNA repair and chromatin remodeling mechanisms in plant genome: an update.Cell Cycle. 2021 Sep;20(18):1760-1784. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2021.1966584. Epub 2021 Aug 26. Cell Cycle. 2021. PMID: 34437813 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plasticity of Meiotic Recombination Rates in Response to Temperature in Arabidopsis.Genetics. 2018 Apr;208(4):1409-1420. doi: 10.1534/genetics.117.300588. Epub 2018 Mar 1. Genetics. 2018. PMID: 29496746 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aboussekhra, A., Biggerstaff, M., Shivji, M.K., Vilpo, J.A., Moncollin, V., Podust, V.N., Protic, M., Hubscher, U., Egly, J.M., and Wood, R.D. (1995). Mammalian DNA nucleotide excision repair reconstituted with purified protein components. Cell 80 859–868. - PubMed
-
- Amasino, R.M. (2005). Vernalization and flowering time. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 16 154–158. - PubMed
-
- Boyko, A., Hudson, D., Bhomkar, P., Kathiria, P., and Kovalchuk, I. (2006). Increase of homologous recombination frequency in vascular tissue of Arabidopsis plants exposed to salt stress. Plant Cell Physiol. 47 736–742. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

