Biosynthesis of a linoleic acid allylic epoxide: mechanistic comparison with its chemical synthesis and leukotriene A biosynthesis
- PMID: 19244216
- PMCID: PMC2694342
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M900025-JLR200
Biosynthesis of a linoleic acid allylic epoxide: mechanistic comparison with its chemical synthesis and leukotriene A biosynthesis
Abstract
Biosynthesis of the leukotriene A (LTA) class of epoxide is a lipoxygenase-catalyzed transformation requiring a fatty acid hydroperoxide substrate containing at least three double bonds. Here, we report on biosynthesis of a dienoic analog of LTA epoxides via a different enzymatic mechanism. Beginning with homolytic cleavage of the hydroperoxide moiety, a catalase/peroxidase-related hemoprotein from Anabaena PCC 7120, which occurs in a fusion protein with a linoleic acid 9R-lipoxygenase, dehydrates 9R-hydroperoxylinoleate to a highly unstable epoxide. Using methods we developed for isolating extremely labile compounds, we prepared and purified the epoxide and characterized its structure as 9R,10R-epoxy-octadeca-11E,13E-dienoate. This epoxide hydrolyzes to stable 9,14-diols that were reported before in linoleate autoxidation (Hamberg, M. 1983. Autoxidation of linoleic acid: Isolation and structure of four dihydroxy octadecadienoic acids. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 752: 353-356) and in incubations with the Anabaena enzyme (Lang, I., C. Göbel, A. Porzel, I. Heilmann, and I. Feussner. 2008. A lipoxygenase with linoleate diol synthase activity from Nostoc sp. PCC 7120. Biochem. J. 410: 347-357). We also prepared an equivalent epoxide from 13S-hydroperoxylinoleate using a "biomimetic" chemical method originally described for LTA(4) synthesis and showed that like LTA(4), the C18.2 epoxide conjugates readily with glutathione, a potential metabolic fate in vivo. We compare and contrast the mechanisms of LTA-type allylic epoxide synthesis by lipoxygenase, catalase/peroxidase, and chemical transformations. These findings provide new insights into the reactions of linoleic acid hydroperoxides and extend the known range of catalytic activities of catalase-related hemoproteins.
Figures
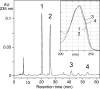
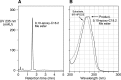



References
-
- Lang I., C. Göbel, A. Porzel, I. Heilmann, and I. Feussner. 2008. A lipoxygenase with linoleate diol synthase activity from Nostoc sp. PCC 7120. Biochem. J. 410 347–357. - PubMed
-
- Zheng Y., W. E. Boeglin, C. Schneider, and A. R. Brash. 2008. A 49 KD mini-lipoxygenase from Anabaena sp. PCC 7120 retains catalytically complete functionality. J. Biol. Chem. 283 5138–5147. - PubMed
-
- Andreou A. Z., M. Vanko, L. Bezakova, and I. Feussner. 2008. Properties of a mini 9R-lipoxygenase from Nostoc sp. PCC 7120 and its mutant forms. Phytochemistry. 69 1832–1837. - PubMed
-
- Liavonchanka A., and I. Feussner. 2006. Lipoxygenases: occurrence, functions and catalysis. J. Plant Physiol. 163 348–357. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

