The 30-amino-acid deletion in the Nsp2 of highly pathogenic porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus emerging in China is not related to its virulence
- PMID: 19244318
- PMCID: PMC2682102
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02678-08
The 30-amino-acid deletion in the Nsp2 of highly pathogenic porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus emerging in China is not related to its virulence
Abstract
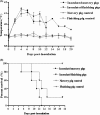
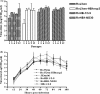
During the past 2 years, an atypical clinical outbreak, caused by a highly pathogenic porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) with a unique 30-amino-acid deletion in its Nsp2-coding region, was pandemic in China. In this study, we generated four full-length infectious cDNA clones: a clone of the highly virulent PRRSV strain JXwn06 (pWSK-JXwn), a clone of the low-virulence PRRSV strain HB-1/3.9 (pWSK-HB-1/3.9), a chimeric clone in which the Nsp2 region containing the 30-amino-acid deletion was replaced by the corresponding region of the low-virulence PRRSV strain HB-1/3.9 (pWSK-JXwn-HB1nsp2), and a mutated HB-1/3.9 clone with the same deletion in Nsp2 as JXwn06 (pWSK-HB1-ND30). We also investigated the pathogenicities of the rescued viruses (designated RvJXwn, RvJXwn-HB1nsp2, RvHB-1/3.9, and RvHB1-ND30, respectively) in specific-pathogen-free piglets in order to determine the role of the 30-amino-acid deletion in the virulence of the highly pathogenic PRRSV. All the rescued viruses could replicate stably in MARC-145 cells. Our findings indicated that RvJXwn-HB1nsp2 retained high virulence for piglets, like RvJXwn and the parental virus JXwn06, although the survival time of piglets infected with RvJXwn-HB1nsp2 was obviously prolonged. RvHB1-ND30 exhibited low virulence for piglets, like RvHB-1/3.9 and the parental virus HB-1/3.9. Therefore, we conclude that the 30-amino-acid deletion is not related to the virulence of the highly pathogenic PRRSV emerging in China.
Figures


References
-
- Albina, E. 1997. Epidemiology of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome (PRRS): an overview. Vet. Microbiol. 55309-316. - PubMed
-
- Allende, R., T. L. Lewis, Z. Lu, D. L. Rock, G. F. Kutish, A. Ali, A. R. Doster, and F. A. Osorio. 1999. North American and European porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome viruses differ in non-structural protein coding regions. J. Gen. Virol. 80307-315. - PubMed
-
- Bautista, E. M., J. J. Meulenberg, C. S. Choi, and T. W. Molitor. 1996. Structural polypeptides of the American (VR-2332) strain of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. Arch. Virol. 1411357-1365. - PubMed
-
- Benfield, D. A., E. Nelson, J. E. Collins, L. Harris, S. M. Goyal, D. Robison, W. T. Christianson, R. B. Morrison, D. E. Gorcyca, and D. W. Chladek. 1992. Characterization of swine infertility and respiratory syndrome (SIRS) virus (isolate ATCC VR-2332). J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 4127-133. - PubMed
-
- Bøtner, A., J. Nielsen, and V. Bille-Hansen. 1994. Isolation of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome (PRRS) virus in a Danish swine herd and experimental infection of pregnant gilts with the virus. Vet. Microbiol. 40351-360. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

