Caveolin-1-mediated suppression of cyclooxygenase-2 via a beta-catenin-Tcf/Lef-dependent transcriptional mechanism reduced prostaglandin E2 production and survivin expression
- PMID: 19244345
- PMCID: PMC2669036
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e08-09-0939
Caveolin-1-mediated suppression of cyclooxygenase-2 via a beta-catenin-Tcf/Lef-dependent transcriptional mechanism reduced prostaglandin E2 production and survivin expression
Abstract
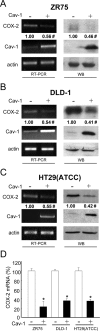
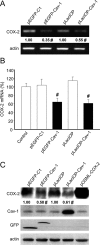
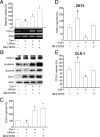
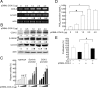
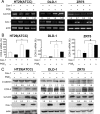
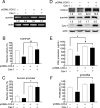
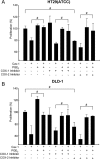
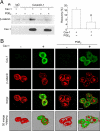
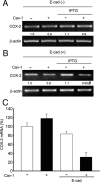
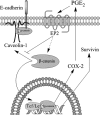
Augmented expression of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and enhanced production of prostaglandin E(2) (PGE(2)) are associated with increased tumor cell survival and malignancy. Caveolin-1 is a scaffold protein that has been proposed to function as a tumor suppressor in human cancer cells, although mechanisms underlying this ability remain controversial. Intriguingly, the possibility that caveolin-1 regulates the expression of COX-2 has not been explored. Here we show that augmented caveolin-1 expression in cells with low basal levels of this protein, such as human colon cancer (HT29, DLD-1), breast cancer (ZR75), and embryonic kidney (HEK293T) cells reduced COX-2 mRNA and protein levels and beta-catenin-Tcf/Lef and COX-2 gene reporter activity, as well as the production of PGE(2) and cell proliferation. Moreover, COX-2 overexpression or PGE(2) supplementation increased levels of the inhibitor of apoptosis protein survivin by a transcriptional mechanism, as determined by PCR analysis, survivin gene reporter assays and Western blotting. Furthermore, addition of PGE(2) to the medium prevented effects attributed to caveolin-1-mediated inhibition of beta-catenin-Tcf/Lef-dependent transcription. Finally, PGE(2) reduced the coimmunoprecipitation of caveolin-1 with beta-catenin and their colocalization at the plasma membrane. Thus, by reducing COX-2 expression, caveolin-1 interrupts a feedback amplification loop involving PGE(2)-induced signaling events linked to beta-catenin/Tcf/Lef-dependent transcription of tumor survival genes including cox-2 itself and survivin.
Figures


Similar articles
-
E-cadherin is required for caveolin-1-mediated down-regulation of the inhibitor of apoptosis protein survivin via reduced beta-catenin-Tcf/Lef-dependent transcription.Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Nov;27(21):7703-17. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01991-06. Epub 2007 Sep 4. Mol Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17785436 Free PMC article.
-
Caveolin-1 controls cell proliferation and cell death by suppressing expression of the inhibitor of apoptosis protein survivin.J Cell Sci. 2006 May 1;119(Pt 9):1812-23. doi: 10.1242/jcs.02894. Epub 2006 Apr 11. J Cell Sci. 2006. PMID: 16608879
-
Survivin expression promotes VEGF-induced tumor angiogenesis via PI3K/Akt enhanced β-catenin/Tcf-Lef dependent transcription.Mol Cancer. 2014 Sep 9;13:209. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-13-209. Mol Cancer. 2014. PMID: 25204429 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium, calcium-sensing receptor and colon cancer.Cancer Lett. 2009 Mar 8;275(1):9-16. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2008.07.001. Epub 2008 Aug 23. Cancer Lett. 2009. PMID: 18725175 Review.
-
Survivin as a global target of intrinsic tumor suppression networks.Cell Cycle. 2009 Sep 1;8(17):2708-10. doi: 10.4161/cc.8.17.9457. Epub 2009 Sep 7. Cell Cycle. 2009. PMID: 19717980 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Caveolin-1 suppresses tumor formation through the inhibition of the unfolded protein response.Cell Death Dis. 2020 Aug 3;11(8):648. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-02792-4. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 32811828 Free PMC article.
-
Epithelium-dependent modulation of responsiveness of airways from caveolin-1 knockout mice is mediated through cyclooxygenase-2 and 5-lipoxygenase.Br J Pharmacol. 2012 Oct;167(3):548-60. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2012.02014.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22551156 Free PMC article.
-
Caveolin-1-Mediated Tumor Suppression Is Linked to Reduced HIF1α S-Nitrosylation and Transcriptional Activity in Hypoxia.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Aug 20;12(9):2349. doi: 10.3390/cancers12092349. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32825247 Free PMC article.
-
New glimpses of caveolin-1 functions in embryonic development and human diseases.Front Biol (Beijing). 2011;6(5):367. doi: 10.1007/s11515-011-1132-8. Epub 2011 Oct 1. Front Biol (Beijing). 2011. PMID: 32215005 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Caveolin-1 function at the plasma membrane and in intracellular compartments in cancer.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2020 Jun;39(2):435-453. doi: 10.1007/s10555-020-09890-x. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2020. PMID: 32458269 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Araki Y., Okamura S., Hussain S. P., Nagashima M., He P., Shiseki M., Miura K., Harris C. C. Regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 expression by the Wnt and ras pathways. Cancer Res. 2003;63:728–734. - PubMed
-
- Backlund M. G., Mann J. R., Dubois R. N. Mechanisms for the prevention of gastrointestinal cancer: the role of prostaglandin E2. Oncology. 2005;69(Suppl 1):28–32. - PubMed
-
- Baratelli F., Krysan K., Heuze-Vourc'h N., Zhu L., Escuadro B., Sharma S., Reckamp K., Dohadwala M., Dubinett S. M. PGE2 confers survivin-dependent apoptosis resistance in human monocyte-derived dendritic cells. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2005;78:555–564. - PubMed
-
- Bender F. C., Reymond M. A., Bron C., Quest A. F. Caveolin-1 levels are down-regulated in human colon tumors, and ectopic expression of caveolin-1 in colon carcinoma cell lines reduces cell tumorigenicity. Cancer Res. 2000;60:5870–5878. - PubMed
-
- Castellone M. D., Teramoto H., Gutkind J. S. Cyclooxygenase-2 and colorectal cancer chemoprevention: the beta-catenin connection. Cancer Res. 2006;66:11085–11088. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

