Soluble HB-EGF induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in inner medullary collecting duct cells by upregulating Snail-2
- PMID: 19244405
- PMCID: PMC2681361
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.90490.2008
Soluble HB-EGF induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in inner medullary collecting duct cells by upregulating Snail-2
Abstract
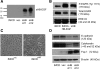
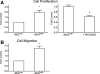
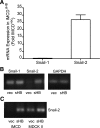
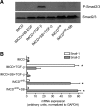
Animal models of acute renal injury suggest that the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) axis may have a beneficial role in the recovery from acute renal injury, but recent reports describe detrimental effects of EGFR activation in chronic renal injury. Expression of the EGFR ligand heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor (HB-EGF) increases following renal injury, but the effects of this sustained upregulation have not been well studied. Here, stable overexpression of soluble HB-EGF (sHB-EGF) in mouse inner medullary collecting duct (IMCD) cells led to marked phenotypic changes: sHB-EGF-expressing cells demonstrated a fibroblast-like morphology, did not form epithelial sheets, exhibited cytoplasmic projections, decreased expression of epithelial markers, and increased expression of fibroblast-specific protein-1. They also demonstrated anchorage-independent growth and formed tumors when injected subcutaneously into nude mice. Quantitative RT-PCR and a luciferase reporter assay suggested that sHB-EGF repressed transcription of E-cadherin, and a concomitant TGF-beta-independent upregulation of the E-cadherin repressor Snail-2 was observed. Stable downregulation of Snail-2 in sHB-EGF-overexpressing cells restored epithelial characteristics (E-cadherin and cytokeratin expression) but did not alter their anchorage-independent growth. In summary, sustained exposure to sHB-EGF induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of IMCD cells, in part by upregulating the E-cadherin transcriptional repressor Snail-2.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Membrane-bound heparin-binding epidermal growth factor like growth factor regulates E-cadherin expression in pancreatic carcinoma cells.Cancer Res. 2007 Sep 15;67(18):8486-93. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-0498. Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17875687
-
Juxtacrine activation of epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor by membrane-anchored heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor protects epithelial cells from anoikis while maintaining an epithelial phenotype.J Biol Chem. 2007 Nov 9;282(45):32890-901. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M702677200. Epub 2007 Sep 11. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17848576
-
A Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG-derived soluble protein, p40, stimulates ligand release from intestinal epithelial cells to transactivate epidermal growth factor receptor.J Biol Chem. 2013 Oct 18;288(42):30742-30751. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.492397. Epub 2013 Sep 16. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 24043629 Free PMC article.
-
Role of glycogen synthase kinase-3 in cell fate and epithelial-mesenchymal transitions.Cells Tissues Organs. 2007;185(1-3):73-84. doi: 10.1159/000101306. Cells Tissues Organs. 2007. PMID: 17587811 Review.
-
Snail family regulation and epithelial mesenchymal transitions in breast cancer progression.J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2010 Jun;15(2):135-47. doi: 10.1007/s10911-010-9179-8. Epub 2010 May 9. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2010. PMID: 20455012 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Establishment and characterization of cetuximab resistant head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell lines: focus on the contribution of the AP-1 transcription factor.Am J Cancer Res. 2015 May 15;5(6):1921-38. eCollection 2015. Am J Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 26269754 Free PMC article.
-
Slug overexpression induces stemness and promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell invasion and metastasis.Oncol Lett. 2014 Jun;7(6):1936-1940. doi: 10.3892/ol.2014.2037. Epub 2014 Apr 4. Oncol Lett. 2014. PMID: 24932263 Free PMC article.
-
Helicobacter pylori potentiates epithelial:mesenchymal transition in gastric cancer: links to soluble HB-EGF, gastrin and matrix metalloproteinase-7.Gut. 2010 Aug;59(8):1037-45. doi: 10.1136/gut.2009.199794. Epub 2010 Jun 28. Gut. 2010. PMID: 20584780 Free PMC article.
-
Shear Stress-Induced Alteration of Epithelial Organization in Human Renal Tubular Cells.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 6;10(7):e0131416. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0131416. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26146837 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor by miR-212 and acquired cetuximab-resistance in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.PLoS One. 2010 Sep 13;5(9):e12702. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012702. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20856931 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barrallo-Gimeno A, Nieto MA. The Snail genes as inducers of cell movement and survival: implications in development and cancer. Development 132: 3151–3161, 2005. - PubMed
-
- Batlle E, Sancho E, Franci C, Dominguez D, Monfar M, Baulida J, Garcia De Herreros A. The transcription factor snail is a repressor of E-cadherin gene expression in epithelial tumour cells. Nat Cell Biol 2: 84–89, 2000. - PubMed
-
- Boutet A, Esteban MA, Maxwell PH, Nieto MA. Reactivation of Snail genes in renal fibrosis and carcinomas: a process of reversed embryogenesis? Cell Cycle 6: 638–642, 2007. - PubMed
-
- Cano A, Perez-Moreno MA, Rodrigo I, Locascio A, Blanco MJ, del Barrio MG, Portillo F, Nieto MA. The transcription factor snail controls epithelial-mesenchymal transitions by repressing E-cadherin expression. Nat Cell Biol 2: 76–83, 2000. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

