The role of Sonic hedgehog of neural origin in thalamic differentiation in the mouse
- PMID: 19244520
- PMCID: PMC6666239
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4524-08.2009
The role of Sonic hedgehog of neural origin in thalamic differentiation in the mouse
Abstract
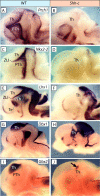
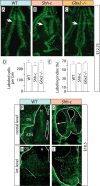
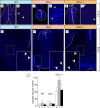
The specification of the intricate neuronal assemblies that characterize the forebrain is not well understood. The ventral spinal cord is specified through a concentration gradient of Sonic hedgehog (Shh) protein secreted by the notochord. Shh is expressed also in the forebrain neuroepithelium (neural Shh) and the underlying notochord and prechordal plate. Neural Shh is essential for the development of the prethalamus (ventral thalamus), but its effects on the thalamus (dorsal thalamus) are still unclear. We hypothesized that neural Shh would act on a previously regionalized dorsal diencephalic region to promote the emergence of specific thalamic nuclear and histological traits. To find out, we generated a conditional mouse mutant line specifically lacking Shh expression in the diencephalic neuroepithelium. We show that the transcription factor Gbx2, required for thalamic development downstream Shh, is expressed in our mutant in a restricted thalamic region and is necessary and sufficient for the differentiation of the medial and intralaminar thalamic nuclei. In the rest of the thalamus, neural Shh is required to promote neuronal aggregation into nuclei as well as axonal extension. In this way, the individual thalamic nuclei show differential dependence on Shh, Gbx2, or both for their differentiation. Additionally, Gbx2 is required for the survival of thalamic neurons.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Differential developmental strategies by Sonic hedgehog in thalamus and hypothalamus.J Chem Neuroanat. 2016 Sep;75(Pt A):20-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jchemneu.2015.11.008. Epub 2015 Dec 12. J Chem Neuroanat. 2016. PMID: 26686294 Review.
-
Spatial and temporal requirements for sonic hedgehog in the regulation of thalamic interneuron identity.Development. 2011 Feb;138(3):531-41. doi: 10.1242/dev.058917. Development. 2011. PMID: 21205797 Free PMC article.
-
Pax6 regulates the formation of the habenular nuclei by controlling the temporospatial expression of Shh in the diencephalon in vertebrates.BMC Biol. 2014 Feb 14;12:13. doi: 10.1186/1741-7007-12-13. BMC Biol. 2014. PMID: 24528677 Free PMC article.
-
Role of neuroepithelial Sonic hedgehog in hypothalamic patterning.J Neurosci. 2009 May 27;29(21):6989-7002. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1089-09.2009. J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19474326 Free PMC article.
-
Sonic hedgehog: a common signal for ventral patterning along the rostrocaudal axis of the neural tube.Int J Dev Biol. 1995 Oct;39(5):809-16. Int J Dev Biol. 1995. PMID: 8645565 Review.
Cited by
-
Establishing Hedgehog Gradients during Neural Development.Cells. 2023 Jan 5;12(2):225. doi: 10.3390/cells12020225. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36672161 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LIM homeobox protein 5 (Lhx5) is essential for mamillary body development.Front Neuroanat. 2015 Oct 27;9:136. doi: 10.3389/fnana.2015.00136. eCollection 2015. Front Neuroanat. 2015. PMID: 26578897 Free PMC article.
-
Patterning and compartment formation in the diencephalon.Front Neurosci. 2012 May 11;6:66. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2012.00066. eCollection 2012. Front Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22593732 Free PMC article.
-
The Ciliopathy Gene Ftm/Rpgrip1l Controls Mouse Forebrain Patterning via Region-Specific Modulation of Hedgehog/Gli Signaling.J Neurosci. 2019 Mar 27;39(13):2398-2415. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2199-18.2019. Epub 2019 Jan 28. J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30692221 Free PMC article.
-
The Tale of the Three Brothers - Shh, Wnt, and Fgf during Development of the Thalamus.Front Neurosci. 2012 May 28;6:76. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2012.00076. eCollection 2012. Front Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22654733 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altman J, Bayer SA. Development of the rat thalamus: I. Mosaic organization of the thalamic neuroepithelium. J Comp Neurol. 1988;275:346–377. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez-Bolado G, Zhou X, Voss AK, Thomas T, Gruss P. Winged helix transcription factor Foxb1 is essential for access of mammillothalamic axons to the thalamus. Development. 2000;127:1029–1038. - PubMed
-
- Andersson E, Tryggvason U, Deng Q, Friling S, Alekseenko Z, Robert B, Perlmann T, Ericson J. Identification of intrinsic determinants of midbrain dopamine neurons. Cell. 2006;124:393–405. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
