L-type calcium channels govern calcium signaling in migrating newborn neurons in the postnatal olfactory bulb
- PMID: 19244525
- PMCID: PMC2677619
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5333-08.2009
L-type calcium channels govern calcium signaling in migrating newborn neurons in the postnatal olfactory bulb
Abstract
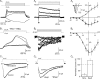
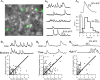
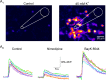
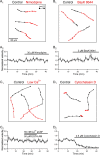
Newborn inhibitory neurons migrate into existing neural circuitry in the olfactory bulb throughout the lifetime of adult mammals. While many factors contribute to the maturation of neural circuits, intracellular calcium is believed to play an important role in regulating cell migration and the development of neural systems. However, the factors underlying calcium signaling within newborn neurons in the postnatal olfactory bulb are not well understood. Here, we show that migrating, immature neurons in the olfactory bulb subependymal layer (SEL) undergo spontaneous and depolarization-evoked intracellular calcium transients mediated by high-voltage-activated L-type calcium channels. In contrast to migrating immature neurons in other brain regions, modulation of calcium transients in SEL cells does not alter their rate of migration.
Figures



References
-
- Bolteus AJ, Garganta C, Bordey A. Assays for measuring extracellular GABA levels and cell migration rate in acute slices. Brain Res Brain Res Protoc. 2005;14:126–134. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
