Heme oxygenase-1 inhibits pro-oxidant induced hypertrophy in HL-1 cardiomyocytes
- PMID: 19244544
- PMCID: PMC2787409
- DOI: 10.3181/0810-RM-312
Heme oxygenase-1 inhibits pro-oxidant induced hypertrophy in HL-1 cardiomyocytes
Abstract
Aims: Reactive oxygen species (ROS) activate multiple signaling pathways involved in cardiac hypertrophy. Since HO-1 exerts potent antioxidant effects, we hypothesized that this enzyme inhibits ROS-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy.
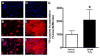
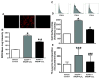
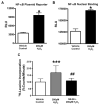
Methods: HL-1 cardiomyocytes were transduced with an adenovirus constitutively expressing HO-1 (AdHO-1) to increase basal HO-1 expression and then exposed to 200 microM hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). Hypertrophy was measured using 3H-leucine incorporation, planar morphometry and cell-size by forward-scatter flow-cytometry. The pro-oxidant effect of H2O2 was assessed by redox sensitive fluorophores. Inducing intracellular redox imbalance resulted in cardiomyocyte hypertrophy through transactivation of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappaB).
Results: Pre-emptive HO-1 overexpression attenuated the redox imbalance and reduced hypertrophic indices. This is the first time that HO-1 has directly been shown to inhibit oxidant-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy by a NF-kappaB-dependent mechanism.
Conclusion: These results demonstrate that HO-1 inhibits pro-oxidant induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy and suggest that HO-1 may yield therapeutic potential in treatment of.
Figures





References
-
- Frey N, Olson EN. Cardiac hypertrophy: the good, the bad and the ugly. Ann Rev Physiol. 2002;65:45–79. - PubMed
-
- Swynghedauw B. Molecular mechanisms of myocardial remodeling. Physiol Rev. 1999;79:215–262. - PubMed
-
- Sawyer DB, Siwik DA, Xiao L, Pimentel DR, Singh K, Colucci WS. Role of oxidative stress in myocardial hypertrophy and failure. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2002;34:379–388. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

