Creatinine kinetics and the definition of acute kidney injury
- PMID: 19244578
- PMCID: PMC2653692
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2008070669
Creatinine kinetics and the definition of acute kidney injury
Abstract
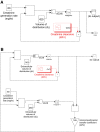
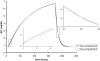
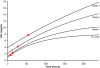
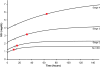
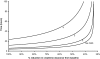
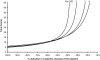
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a common and devastating medical condition, but no widely accepted definition exists. A recent classification system by the Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative (RIFLE) defines AKI largely by percentage increases in serum creatinine (SCr) over baseline. The Acute Kidney Injury Network defines the first stage by either an absolute or a percentage increase in SCr. To examine the implications of various definitions, we solved differential equations on the basis of mass balance principles. We simulated creatinine kinetics after AKI in the setting of normal baseline kidney function and stages 2, 3, and 4 chronic kidney disease (CKD). The percentage changes in SCr after severe AKI are highly dependent on baseline kidney function. Twenty-four hours after a 90% reduction in creatinine clearance, the rise in SCr was 246% with normal baseline kidney function, 174% in stage 2 CKD, 92% in stage 3 CKD, and only 47% in stage 4 CKD. By contrast, the absolute increase was nearly identical (1.8 to 2.0 mg/dl) across the spectrum of baseline kidney function. Time to reach a 50% increase in SCr was directly related to baseline kidney function: From 4 h (normal baseline) up to 27 h for stage 4 CKD. By contrast, the time to reach a 0.5-mg/dl increase in SCr was virtually identical after moderate to severe AKI (>50% reduction in creatinine clearance). We propose an alternative definition of AKI that incorporates absolute changes in SCr over a 24- to 48-h time period.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of absolute serum creatinine changes versus Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes consensus definitions for characterizing stages of acute kidney injury.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2013 Jun;28(6):1447-54. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfs533. Epub 2013 Jan 25. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2013. PMID: 23355628 Free PMC article.
-
Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes or creatinine kinetics criteria in acute kidney injury: a proof of concept study.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2013 Nov;28(11):2779-87. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gft375. Epub 2013 Sep 5. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2013. PMID: 24009288
-
Impact of a new definition of acute kidney injury based on creatinine kinetics in cardiac surgery patients: a comparison with the RIFLE classification.Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2015 Mar;20(3):338-44. doi: 10.1093/icvts/ivu393. Epub 2014 Dec 1. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2015. PMID: 25452556
-
The definitions and staging systems of acute kidney injury and their limitations in practice.Arab J Nephrol Transplant. 2013 Sep;6(3):145-52. Arab J Nephrol Transplant. 2013. PMID: 24053740 Review.
-
Biomarkers of renal function, which and when?Clin Chim Acta. 2015 Jan 1;438:350-7. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2014.08.039. Epub 2014 Sep 3. Clin Chim Acta. 2015. PMID: 25195004 Review.
Cited by
-
The case for precision dosing: medical conservatism does not justify inaction.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2021 Jun 18;76(7):1661-1665. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkab086. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2021. PMID: 33843994 Free PMC article.
-
Estimating kidney function in the critically ill patients.Crit Care Res Pract. 2013;2013:721810. doi: 10.1155/2013/721810. Epub 2013 May 8. Crit Care Res Pract. 2013. PMID: 23862059 Free PMC article.
-
Urinary Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin Predicts Intensive Care Unit Admission Diagnosis: A Prospective Cohort Study.Kidney360. 2022 Jul 13;3(9):1502-1510. doi: 10.34067/KID.0001492022. eCollection 2022 Sep 29. Kidney360. 2022. PMID: 36245663 Free PMC article.
-
Use of postoperative creatinine to predict sustained kidney injury in patients undergoing mesothelioma surgery.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012 Jul;7(7):1071-8. doi: 10.2215/CJN.12401211. Epub 2012 Apr 26. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012. PMID: 22537654 Free PMC article.
-
Incidence of and Risk Factors for Acute Kidney Injury During Antituberculosis Treatment: A Prospective Cohort Study and Literature Review.Infect Dis Ther. 2023 Mar;12(3):919-931. doi: 10.1007/s40121-023-00761-w. Epub 2023 Feb 11. Infect Dis Ther. 2023. PMID: 36773200 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kellum JA, Bellomo R, Ronco C, Mehta R, Clark W, Levin NW: The 3rd International Consensus Conference of the Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative (ADQI). Int J Artif Organs 28: 441–444, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Molitoris BA, Levin A, Warnock DG, Joannidis M, Mehta RL, Kellum JA, Ronco C, Shah SV: Improving outcomes of acute kidney injury: report of an initiative. Nat Clin Pract Nephrol 3: 439–442, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Chiou WL, Hsu FH: Pharmacokinetics of creatinine in man and its implications in the monitoring of renal function and in dosage regimen modifications in patients with renal insufficiency. J Clin Pharmacol 15: 427–434, 1975 - PubMed
-
- Moran SM, Myers BD: Course of acute renal failure studied by a model of creatinine kinetics. Kidney Int 27: 928–937, 1985 - PubMed
-
- Coresh J, Selvin E, Stevens LA, Manzi J, Kusek JW, Eggers P, Van Lente F, Levey AS: Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in the United States. JAMA 298: 2038–2047, 2007 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

