Optimization of a murine immunization model for study of PF4/heparin antibodies
- PMID: 19245419
- PMCID: PMC3711941
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2009.03330.x
Optimization of a murine immunization model for study of PF4/heparin antibodies
Abstract
Summary background: Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) is a life-threatening thrombotic illness caused by drug-dependent antibodies recognizing complexes of platelet factor 4 (PF4) and heparin. Little is known about the immune pathogenesis of HIT, in particular factors influencing PF4/heparin antibody formation. To gain insight into the biologic basis of heparin sensitization, we have recently developed an animal model using wild-type (WT) mice in which murine PF4/heparin antibodies (anti-mPF4/H) arise de novo after antigen challenge.
Objectives and methods: This report describes technical refinements to the murine model and describes additional biologic features of the immune response to mPF4/heparin.
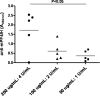
Results: Our studies indicate that antibody responses to mPF4/heparin are dependent on murine strain, injection routes and doses of mPF4 and heparin. C57BL/6 mice are more immunologically responsive to mPF4/heparin antigen than BALB/c mice and robust immunization can be achieved with intravenous, but not intraperitoneal, administration of antigen. We also observe a direct relationship between initial concentrations of mPF4 and antibody levels. Additionally, we demonstrate that mPF4/H immune response in mice decays with time, is not associated with thrombocytopenia and displays characteristics of immune recall on re-exposure to antigen.
Conclusions: These studies describe and characterize a murine model for studying the immunologic basis of PF4/heparin sensitization.
Figures

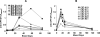




References
-
- Martel N, Lee J, Wells PS. Risk for heparin-induced thrombocytopenia with unfractionated and low-molecular-weight heparin thromboprophylaxis: a meta-analysis. Blood. 2005;106:2710–5. - PubMed
-
- Arepally GM, Ortel TL. Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:809–17. - PubMed
-
- Amiral J, Peynaud-Debayle E, Wolf M, Bridey F, Vissac AM, Meyer D. Generation of antibodies to heparin-PF4 complexes without thrombocytopenia in patients treated with unfractionated or low-molecular-weight heparin. Am J Hematol. 1996;52:90–5. - PubMed
-
- Bauer TL, Arepally G, Konkle BA, Mestichelli B, Shapiro SS, Cines DB, Poncz M, McNulty S, Amiral J, Hauck WW, Edie RN, Mannion JD. Prevalence of heparin-associated antibodies without thrombosis in patients undergoing cardiopulmonary bypass surgery. Circulation. 1997;95:1242–6. - PubMed
-
- Reilly MP, Taylor SM, Hartman NK, Arepally GM, Sachais BS, Cines DB, Poncz M, McKenzie SE. Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia/thrombosis in a transgenic mouse model requires human platelet factor 4 and platelet activation through FcgammaRIIA. Blood. 2001;98:2442–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

