Effect of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha on transcription of survivin in non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 19245702
- PMCID: PMC2663545
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-9966-28-29
Effect of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha on transcription of survivin in non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
Background: Survivin is a structurally and functionally unique member of the inhibitor of apoptosis protein (IAP) family. It plays an important role, not only in regulating mitosis but also in inhibiting apoptosis. The current literature contains few reports on the transcriptional regulation of survivin expression in lung cancer.
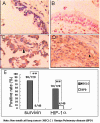
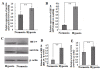
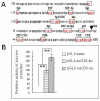
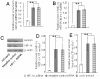
Methods: In this study, we investigated the effect of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha (HIF-1alpha) on the transcriptional activity of the survivin promoter in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Immunohistochemical staining was used to detect the expression of survivin and HIF-1alpha in the lung tissue of 120 patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and 40 patients with benign pulmonary disease. We also performed experiments with the lung adenocarcinoma cell line A549 cells, which were cultured under hypoxic conditions. The expression of survivin and HIF-1alpha was detected by real-time RT-PCR and Western blotting. In the survivin promoter the putative binding-site for HIF-1alpha, is -19 bpapproximately -16 bp upstream of TSS. We performed site-directed mutagenesis of this binding site, and used luciferase reporter plasmids to determine the relative activity of the survivin promoter in A549 cells. We also studied the effect of HIF-1alpha on the expression of survivin by dsRNA targeting of HIF-1alpha mRNA.
Results: HIF-1alpha (58.33%) and survivin (81.60%) were both over-expressed in NSCLC and their expressions correlated with one another. They were also expressed in A549 cells under normal and hypoxic conditions, with a significant increase under hypoxic conditions. Site directed mutagenesis of the putative binding site for HIF-1alpha in the survivin promoter significantly decreased the activity of the survivin promoter in A549 cells. Inhibition of HIF-1alpha by RNAi decreased the expression of survivin in A549 cell lines.
Conclusion: Our results indicate that the binding of HIF-1alpha to the survivin promoter increases transcription of the survivin gene. Thus, HIF-1alpha is an important transcriptional regulator of survivin expression.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

