Delivery of CD44 shRNA/nanoparticles within cancer cells: perturbation of hyaluronan/CD44v6 interactions and reduction in adenoma growth in Apc Min/+ MICE
- PMID: 19246453
- PMCID: PMC2673310
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M806772200
Delivery of CD44 shRNA/nanoparticles within cancer cells: perturbation of hyaluronan/CD44v6 interactions and reduction in adenoma growth in Apc Min/+ MICE
Abstract
Our studies have shown that constitutive interactions between hyaluronan and CD44 on tumor cells induces various anti-apoptotic cell survival pathways through the formation of a multimeric signaling complex that contains activated receptor tyrosine kinases. Inhibition of the hyaluronan-CD44 interactions on tumor cells by hyaluronan-CD44 interaction antagonists suppresses these activities by disassembling the complex. Although the anti-tumor activity of hyaluronan-oligosaccharides, a hyaluronan-CD44 interaction antagonist, is effective in sensitizing tumor cells to chemotherapeutic agents and reducing tumor growth in xenografts, hyaluronan-oligosaccharide alone was not effective in reducing tumor progression in Apc Min/+ mice. We now show in vitro and in vivo that targeted inhibition of the expression of CD44v6 depletes the ability of the colon tumor cells to signal through hyaluronan-CD44v6 interactions. First, we cloned oligonucleotides coding CD44v6 shRNA into a conditionally silenced pSico vector. Second, using pSico-CD44v6 shRNA and a colon-specific Fabpl promoter-driven Cre recombinase expression vector packaged into transferrin-coated nanoparticles, we successfully delivered the CD44v6 shRNA within pre-neoplastic and neoplastic colon malignant cells. Third, using the Apc Min/+ mice model, we demonstrated that inhibition of the CD44v6 expression reduces the signaling through a hyaluronan/CD44v6-pErbB2-Cox-2 interaction pathway and reduced adenoma number and growth. Together, these data provide insight into the novel therapeutic strategies of short hairpin RNA/nanoparticle technology and its potential for silencing genes associated with colon tumor cells.
Figures


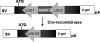







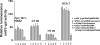


References
-
- Markwald, R. R., Fitzharris, T. P., Bank, H., and Bernanke, D. H. (1978) Dev. Biol. 62 292-316 - PubMed
-
- Lee, J. Y., and Spicer, A. P. (2000) Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 12 581-586 - PubMed
-
- Toole, B. P. (2004) Nat. Rev. Cancer 4 528-539 - PubMed
-
- Hascall, V. C., Majors, A. K., De La Motte, C. A., Evanko, S. P., Wang, A., Drazba, J. A., Strong, S. A., and Wight, T. N. (2004) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1673 3-12 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

