Increased insulin sensitivity in mice lacking collectrin, a downstream target of HNF-1alpha
- PMID: 19246514
- PMCID: PMC2691681
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2008-0274
Increased insulin sensitivity in mice lacking collectrin, a downstream target of HNF-1alpha
Abstract
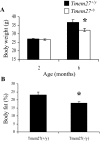
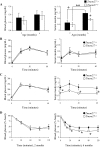
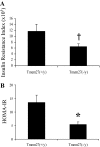
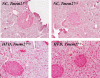
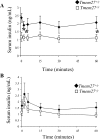
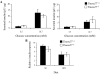
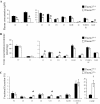
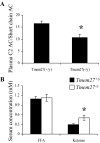
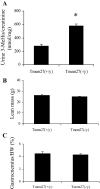
Collectrin is a downstream target of the transcription factor hepatocyte nuclear factor-1alpha (HNF-1alpha), which is mutated in maturity-onset diabetes of the young subtype 3 (MODY3). Evidence from transgenic mouse models with collectrin overexpression in pancreatic islets suggests divergent roles for collectrin in influencing beta-cell mass and insulin exocytosis. To clarify the function of collectrin in the pancreas, we used a mouse line with targeted deletion of the gene. We examined pancreas morphology, glucose homeostasis by ip glucose tolerance testing (IPGTT) and insulin tolerance testing (IPITT), and pancreas function by in vivo acute-phase insulin response determination and glucose-stimulated insulin secretion from isolated islets. We find no difference in either pancreas morphology or function between wild-type and collectrin-deficient animals (Tmem27(-/y)). However, we note that by 6 months of age, Tmem27(-/y) mice exhibit increased insulin sensitivity by IPITT and decreased adiposity by dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry scanning compared with wild-type. We have previously reported that Tmem27(-/y) mice exhibit profound aminoaciduria due to failed renal recovery. We now demonstrate that Tmem27(-/y) animals also display inappropriate excretion of some short-chain acylcarnitines derived from amino acid and fatty acid oxidation. We provide further evidence for compensatory up-regulation of oxidative metabolism in Tmem27(-/y) mice, along with enhanced protein turnover associated with preserved lean mass even out to 1.5 yr of age. Our studies suggest that collectrin-deficient mice activate a number of adaptive mechanisms to defend energy homeostasis in the setting of ongoing nutrient losses.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The HNF-1 target collectrin controls insulin exocytosis by SNARE complex formation.Cell Metab. 2005 Dec;2(6):373-84. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2005.11.003. Cell Metab. 2005. PMID: 16330323
-
Tmem27: a cleaved and shed plasma membrane protein that stimulates pancreatic beta cell proliferation.Cell Metab. 2005 Dec;2(6):385-97. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2005.11.001. Cell Metab. 2005. PMID: 16330324
-
The HNF-1alpha-SNARE connection.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2007 Nov;9 Suppl 2:40-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1463-1326.2007.00773.x. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2007. PMID: 17919177
-
Roles of HNF1α and HNF4α in pancreatic β-cells: lessons from a monogenic form of diabetes (MODY).Vitam Horm. 2014;95:407-23. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-800174-5.00016-8. Vitam Horm. 2014. PMID: 24559927 Review.
-
Role of collectrin, an ACE2 homologue, in blood pressure homeostasis.Curr Hypertens Rep. 2014 Nov;16(11):490. doi: 10.1007/s11906-014-0490-4. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2014. PMID: 25182162 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Heteromeric Solute Carriers: Function, Structure, Pathology and Pharmacology.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;21:13-127. doi: 10.1007/5584_2020_584. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 33052588 Review.
-
Identification of known and novel pancreas genes expressed downstream of Nkx2.2 during development.BMC Dev Biol. 2009 Dec 10;9:65. doi: 10.1186/1471-213X-9-65. BMC Dev Biol. 2009. PMID: 20003319 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of novel inhibitors of the amino acid transporter B0 AT1 (SLC6A19), a potential target to induce protein restriction and to treat type 2 diabetes.Br J Pharmacol. 2017 Mar;174(6):468-482. doi: 10.1111/bph.13711. Epub 2017 Feb 14. Br J Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28176326 Free PMC article.
-
Pancreatic islet and progenitor cell surface markers with cell sorting potential.Diabetologia. 2012 Jan;55(1):154-65. doi: 10.1007/s00125-011-2295-1. Epub 2011 Sep 23. Diabetologia. 2012. PMID: 21947380
-
Classical Renin-Angiotensin system in kidney physiology.Compr Physiol. 2014 Jul;4(3):1201-28. doi: 10.1002/cphy.c130040. Compr Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24944035 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Giuffrida FM, Reis AF 2005 Genetic and clinical characteristics of maturity-onset diabetes of the young. Diabetes Obes Metab 7:318–326 - PubMed
-
- Yamagata K, Oda N, Kaisaki PJ, Menzel S, Furuta H, Vaxillaire M, Southam L, Cox RD, Lathrop GM, Boriraj VV, Chen X, Cox NJ, Oda Y, Yano H, Le Beau MM, Yamada S, Nishigori H, Takeda J, Fajans SS, Hattersley AT, Iwasaki N, Hansen T, Pedersen O, Polonsky KS, Turner RC, Velho G, Chevre J-C, Froguel P, Bell GI 1996 Mutations in the hepatocyte nuclear factor-1α gene in maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY3). Nature 384:455–458 - PubMed
-
- Blumenfeld M, Maury M, Chouard T, Yaniv M, Condamine H 1991 Hepatic nuclear factor 1 (HNF1) shows a wider distribution than products of its known target genes in developing mouse. Development 113:589–599 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

