The FGF family: biology, pathophysiology and therapy
- PMID: 19247306
- PMCID: PMC3684054
- DOI: 10.1038/nrd2792
The FGF family: biology, pathophysiology and therapy
Abstract
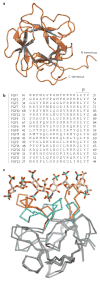
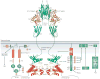
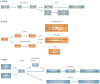
The family of fibroblast growth factors (FGFs) regulates a plethora of developmental processes, including brain patterning, branching morphogenesis and limb development. Several mitogenic, cytoprotective and angiogenic therapeutic applications of FGFs are already being explored, and the recent discovery of the crucial roles of the endocrine-acting FGF19 subfamily in bile acid, glucose and phosphate homeostasis has sparked renewed interest in the pharmacological potential of this family. This Review discusses traditional applications of recombinant FGFs and small-molecule FGF receptor kinase inhibitors in the treatment of cancer and cardiovascular disease and their emerging potential in the treatment of metabolic syndrome and hypophosphataemic diseases.
Figures
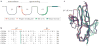
References
-
- Itoh N, Ornitz DM. Evolution of the Fgf and Fgfr gene families. Trends Genet. 2004;20:563–569. - PubMed
-
- Olsen SK, et al. Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) homologous factors share structural but not functional homology with FGFs. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:34226–34236. - PubMed
-
- Fu L, et al. Fibroblast growth factor19 increases metabolic rate and reverses dietary and leptin-deficient diabetes. Endocrinology. 2004;145:2594–2603. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

