HIV induces TRAIL sensitivity in hepatocytes
- PMID: 19247452
- PMCID: PMC2644790
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0004623
HIV induces TRAIL sensitivity in hepatocytes
Abstract
Background: HIV infected patients have an increased susceptibility to liver disease due to Hepatitis B Virus (HBV), Hepatitis C Virus (HCV), alcoholic, and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Clinically, this results in limited options for antiretroviral therapy and accelerated rates of liver disease, causing liver disease to be the second leading cause of death for HIV infected patients. The mechanisms causing this propensity for liver dysfunction during HIV remains unknown.
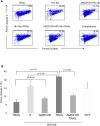
Methodology/principal findings: We demonstrate that HIV and/or the HIV glycoprotein gp120 ligation of CXCR4 on hepatocytes selectively up-regulates TRAIL R2 expression and confers an acquired sensitivity to TRAIL mediated apoptosis which is mediated by JNK II, but not p38 nor G-proteins.
Conclusions/significance: These findings suggest that HIV infection renders hepatocytes more susceptible to liver injury during disease states associated with enhanced TRAIL production such as HBV, HCV, or steatohepatitis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Sulkowski MS. Management of hepatic complications in HIV-infected persons. J Infect Dis. 2008;197(Suppl 3):S279–293. - PubMed
-
- Weber R, Sabin CA, Friis-Moller N, Reiss P, El-Sadr WM, et al. Liver-related deaths in persons infected with the human immunodeficiency virus: the D:A:D study. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166:1632–1641. - PubMed
-
- Bongiovanni M, Tordato F. Steatohepatitis in HIV-infected subjects: pathogenesis, clinical impact and implications in clinical management. Curr HIV Res. 2007;5:490–498. - PubMed
-
- Janssen HL, Higuchi H, Abdulkarim A, Gores GJ. Hepatitis B virus enhances tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) cytotoxicity by increasing TRAIL-R1/death receptor 4 expression. J Hepatol. 2003;39:414–420. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

