Chloride intracellular channel 4 is involved in endothelial proliferation and morphogenesis in vitro
- PMID: 19247789
- PMCID: PMC3893792
- DOI: 10.1007/s10456-009-9139-3
Chloride intracellular channel 4 is involved in endothelial proliferation and morphogenesis in vitro
Abstract
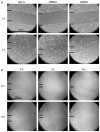
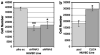
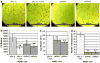
New capillaries are formed through angiogenesis and an integral step in this process is endothelial tubulogenesis. The molecular mechanisms driving tube formation during angiogenesis are not yet delineated. Recently, the chloride intracellular channel 4 (CLIC4)-orthologue EXC-4 was found to be necessary for proper development and maintenance of the Caenorhabditis elegans excretory canal, implicating CLIC4 as a regulator of tubulogenesis. Here, we studied the role of CLIC4 in angiogenesis and endothelial tubulogenesis. We report the effects of inhibiting or inducing CLIC4 expression on distinct aspects of endothelial cell behavior in vitro. Our experiments utilized RNA interference to establish cultured human endothelial cell lines with significant reduction of CLIC4 expression, and a CLIC4-expressing lentiviral plasmid was used to establish CLIC4 overexpression in endothelial cells. We observed no effect on cell migration and a modest effect on cell survival. Reduced CLIC4 expression decreased cell proliferation, capillary network formation, capillary-like sprouting, and lumen formation. This suggests that normal endogenous CLIC4 expression is required for angiogenesis and tubulogenesis. Accordingly, increased CLIC4 expression promoted proliferation, network formation, capillary-like sprouting, and lumen formation. We conclude that CLIC4 functions to promote endothelial cell proliferation and to regulate endothelial morphogenesis, and is thus involved in multiple steps of in vitro angiogenesis.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

