The therapeutic potential of novel cannabinoid receptors
- PMID: 19248809
- PMCID: PMC3685492
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2009.01.005
The therapeutic potential of novel cannabinoid receptors
Abstract
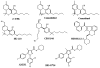
Cannabinoids produce a plethora of biological effects, including the modulation of neuronal activity through the activation of CB(1) receptors and of immune responses through the activation of CB(2) receptors. The selective targeting of either of these two receptor subtypes has clear therapeutic value. Recent evidence indicates that some of the cannabinomimetic effects previously thought to be produced through CB(1) and/or CB(2) receptors, be they on neuronal activity, on the vasculature tone or immune responses, still persist despite the pharmacological blockade or genetic ablation of CB(1) and/or CB(2) receptors. This suggests that additional cannabinoid and cannabinoid-like receptors exist. Here we will review this evidence in the context of their therapeutic value and discuss their true belonging to the endocannabinoid signaling system.
Figures

References
-
- Abadji V, Lin S, Taha G, Griffin G, Stevenson LA, Pertwee RG, Makriyannis A. (R)-methanandamide: a chiral novel anandamide possessing higher potency and metabolic stability. J Med Chem. 1994;37:1889–1893. - PubMed
-
- Adams IB, Compton DR, Martin BR. Assessment of anandamide interaction with the cannabinoid brain receptor: SR 141716A antagonism studies in mice and autoradiographic analysis of receptor binding in rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1998;284:1209–17. - PubMed
-
- Adams IB, Ryan W, Singer M, Thomas BF, Compton DR, Razdan RK, Martin BR. Evaluation of cannabinoid receptor binding and in vivo activities for anandamide analogs. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1995;273:1172–81. - PubMed
-
- Baker D, Pryce G, Davies WL, Hiley CR. In silico patent searching reveals a new cannabinoid receptor. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2006;27:1–4. - PubMed
-
- Bayewitch M, Rhee MH, Avidor-Reiss T, Breuer A, Mechoulam R, Vogel Z. (-)-Delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol antagonizes the peripheral cannabinoid receptor-mediated inhibition of adenylyl cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:9902–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

