Intrahippocampal administration of an NMDA-receptor antagonist impairs spatial discrimination reversal learning in weanling rats
- PMID: 19248837
- PMCID: PMC2680934
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nlm.2009.02.005
Intrahippocampal administration of an NMDA-receptor antagonist impairs spatial discrimination reversal learning in weanling rats
Abstract
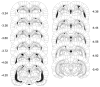
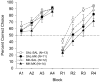
Systemic administration of MK-801, an NMDA-receptor antagonist, impairs reversal learning in weanling rats [Chadman, K.K., Watson, D.J., & Stanton, M.E. (2006). NMDA-receptor antagonism impairs reversal learning in developing rats. Behavioral Neuroscience, 120(5), 1071-1083]. The brain systems responsible for this effect are not known in either adult or young animals. This study tested the hypothesis that hippocampal NMDA receptors are engaged in weanling-age rats during spatial discrimination reversal training in a T-maze. In Experiment 1, 26-day-old Long-Evans rats (P26) showed a dose-related impairment on this task following bilateral intrahippocampal administration of either 2.5 or 5.0microg MK-801 or saline vehicle during the reversal training phase only. In Experiment 2, P26 rats were trained on the same task, but received intrahippocampal MK-801 (2.5microg) during acquisition, reversal, both, or neither. MK-801 failed to impair acquisition, ruling out nonspecific "performance effects" of the drug. MK-801 impaired reversal irrespective of drug treatment during acquisition. NMDA-receptor antagonism in the hippocampus is sufficient to account for the previously reported effects of systemic MK-801 on reversal of T-maze position discrimination.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Medial prefrontal administration of MK-801 impairs T-maze discrimination reversal learning in weanling rats.Behav Brain Res. 2009 Dec 14;205(1):57-66. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2009.07.026. Epub 2009 Jul 28. Behav Brain Res. 2009. PMID: 19643149 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial discrimination reversal learning in weanling rats is impaired by striatal administration of an NMDA-receptor antagonist.Learn Mem. 2009 Aug 27;16(9):564-72. doi: 10.1101/lm.1448009. Print 2009 Sep. Learn Mem. 2009. PMID: 19713355 Free PMC article.
-
NMDA receptor antagonism impairs reversal learning in developing rats.Behav Neurosci. 2006 Oct;120(5):1071-83. doi: 10.1037/0735-7044.120.5.1071. Behav Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 17014258 Free PMC article.
-
NMDA receptor involvement in spatial delayed alternation in developing rats.Behav Neurosci. 2009 Feb;123(1):44-53. doi: 10.1037/a0013633. Behav Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19170429 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of dizocilpine (MK-801) on conditional discrimination learning in the rat.Behav Pharmacol. 1997 Oct;8(5):383-8. Behav Pharmacol. 1997. PMID: 9832977
Cited by
-
NMDA receptors and the ontogeny of post-shock and retention freezing during contextual fear conditioning.Dev Psychobiol. 2020 Apr;62(3):380-385. doi: 10.1002/dev.21928. Epub 2019 Oct 17. Dev Psychobiol. 2020. PMID: 31621064 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical physiology and mechanism of dizocilpine (MK-801): electron transfer, radicals, redox metabolites and bioactivity.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2010 Jan-Feb;3(1):13-22. doi: 10.4161/oxim.3.1.10028. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2010. PMID: 20716924 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Granulocyte colony stimulating factor reduces brain injury in a cardiopulmonary bypass-circulatory arrest model of ischemia in a newborn piglet.Neurochem Res. 2014 Nov;39(11):2085-92. doi: 10.1007/s11064-014-1399-7. Epub 2014 Aug 1. Neurochem Res. 2014. PMID: 25082120 Free PMC article.
-
Reversal Training Discloses Gender Differences in a Spatial Memory Task in Humans.Brain Sci. 2023 Apr 29;13(5):740. doi: 10.3390/brainsci13050740. Brain Sci. 2023. PMID: 37239212 Free PMC article.
-
Treadmill Exercise Training Ameliorates Apoptotic Cells and DNA Oxidation in the Cerebral Cortex of Rats Exposed to Chronic Ketamine Abuse.Addict Biol. 2025 Mar;30(3):e70025. doi: 10.1111/adb.70025. Addict Biol. 2025. PMID: 40062767 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahlander M, Misane I, Schott PA, Ogren SO. A behavioral analysis of the spatial learning deficit induced by the NMDA receptor antagonist MK-801 (dizocilpine) in the rat. Neuropsychopharmacology. 1999;21(3):414–26. - PubMed
-
- Bardgett ME, Boeckman R, Krochmal D, Fernando H, Ahrens R, Csernansky JG. NMDA receptor blockade and hippocampal neuronal loss impair fear conditioning and position habit reversal in C57Bl/6 mice. Brain Research Bulletin. 2003;60(1–2):131–42. - PubMed
-
- Bouton ME. Context and behavioral processes in extinction. Learning and Memory. 2004;11(5):485–94. - PubMed
-
- Caramanos Z, Shapiro ML. Spatial memory and N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists APV and MK-801: memory impairments depend on familiarity with the environment, drug dose, and training duration. Behavioral Neuroscience. 1994;108(1):30–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

